The RIM101 pathway contributes to yeast cell wall assembly and its function becomes essential in the absence of mitogen-activated protein kinase Slt2p
- PMID: 16524906
- PMCID: PMC1398071
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.5.3.507-517.2006
The RIM101 pathway contributes to yeast cell wall assembly and its function becomes essential in the absence of mitogen-activated protein kinase Slt2p
Abstract
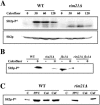
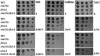
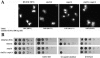
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae ynl294cDelta (rim21Delta) mutant was identified in our lab owing to its moderate resistance to calcofluor, although it also displayed all of the phenotypic traits associated with its function as the putative sensor (Rim21p) of the RIM101 pathway. rim21Delta also showed moderate hypersensitivity to sodium dodecyl sulfate, caffeine, and zymolyase, and the cell wall compensatory response in this mutant was very poor, as indicated by the almost complete absence of Slt2 phosphorylation and the modest increase in chitin synthesis after calcofluor treatment. However, the cell integrity pathway appeared functional after caffeine treatment or thermal stress. rim21Delta and rim101Delta mutant strains shared all of the cell-wall-associated phenotypes, which were reverted by the expression of Rim101-531p, the constitutively active form of this transcription factor. Therefore, the absence of a functional RIM101 pathway leads to cell wall defects. rim21Delta, as well as rim101Delta, was synthetic lethal with slt2Delta, a synthetic defect alleviated by osmotic stabilization of the media. The double mutants grown in osmotically stabilized media were extremely hypersensitive to zymolyase and showed thicker cell walls, with poorly defined mannoprotein layers. In contrast, rim21Delta rlm1Delta and rim101Delta rlm1Delta double mutants were fully viable. Taken together, these results show that the RIM101 pathway participates directly in cell wall assembly and that it acts in parallel with the protein kinase C pathway (PKC) in this process independently of the transcriptional effect of the compensatory response mediated by this route. In addition, these results provide new experimental evidence of the direct involvement of the PKC signal transduction pathway through the Sltp2 kinase in the construction of yeast cell walls.
Figures


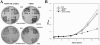


Similar articles
-
Slt2 and Rim101 contribute independently to the correct assembly of the chitin ring at the budding yeast neck in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Sep;8(9):1449-59. doi: 10.1128/EC.00153-09. Epub 2009 Jul 24. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 19633265 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast protein kinase C cell integrity pathway mediates tolerance to the antifungal drug caspofungin through activation of Slt2p mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling.Eukaryot Cell. 2003 Dec;2(6):1200-10. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.6.1200-1210.2003. Eukaryot Cell. 2003. PMID: 14665455 Free PMC article.
-
Cell wall perturbation in yeast results in dual phosphorylation of the Slt2/Mpk1 MAP kinase and in an Slt2-mediated increase in FKS2-lacZ expression, glucanase resistance and thermotolerance.Microbiology (Reading). 2000 Sep;146 ( Pt 9):2121-2132. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-9-2121. Microbiology (Reading). 2000. PMID: 10974100
-
Our paths might cross: the role of the fungal cell wall integrity pathway in stress response and cross talk with other stress response pathways.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Nov;8(11):1616-25. doi: 10.1128/EC.00193-09. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 19717745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell wall integrity signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005 Jun;69(2):262-91. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.2.262-291.2005. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15944456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane transporters and protein traffic networks differentially affecting metal tolerance: a genomic phenotyping study in yeast.Genome Biol. 2008 Apr 7;9(4):R67. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-4-r67. Genome Biol. 2008. PMID: 18394190 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the pH signaling transcription factor PacC in Wangiella (Exophiala) dermatitidis.Fungal Genet Biol. 2009 Sep;46(9):657-66. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2009.05.004. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Fungal Genet Biol. 2009. PMID: 19501183 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways coordinating the alkaline pH response confer resistance to the hevein-type plant antimicrobial peptide Pn-AMP1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Planta. 2016 Dec;244(6):1229-1240. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2579-2. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Planta. 2016. PMID: 27510723
-
Yeast functional genomic screens lead to identification of a role for a bacterial effector in innate immunity regulation.PLoS Pathog. 2007 Feb;3(2):e21. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030021. PLoS Pathog. 2007. PMID: 17305427 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptococcus neoformans Rim101 is associated with cell wall remodeling and evasion of the host immune responses.mBio. 2013 Jan 15;4(1):e00522-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00522-12. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23322637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso-Monge, R., l. E. Rea, I. Wojda, J. P. Bebelman, W. H. Mager, and M. Siderius. 2001. Hyperosmotic stress response and regulation of cell wall integrity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae share common functional aspects. Mol. Microbiol. 41:717-730. - PubMed
-
- Bensen, E. S., S. J. Martin, M. Li, J. Berman, and D. A. Davis. 2004. Transcriptional profiling in Candida albicans reveals new adaptive responses to extracellular pH and functions for Rim101p. Mol. Microbiol. 54:1335-1351. - PubMed
-
- Cabib, E., and A. Duran. 2005. Synthase III-dependent chitin is bound to different acceptors depending on location on the cell wall of budding yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 280:9170-9179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

