Genome-wide analysis of re-replication reveals inhibitory controls that target multiple stages of replication initiation
- PMID: 16525018
- PMCID: PMC1446079
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-11-1037
Genome-wide analysis of re-replication reveals inhibitory controls that target multiple stages of replication initiation
Abstract
DNA replication must be tightly controlled during each cell cycle to prevent unscheduled replication and ensure proper genome maintenance. The currently known controls that prevent re-replication act redundantly to inhibit pre-replicative complex (pre-RC) assembly outside of the G1-phase of the cell cycle. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been a useful model organism to study how eukaryotic cells prevent replication origins from reinitiating during a single cell cycle. Using a re-replication-sensitive strain and DNA microarrays, we map sites across the S. cerevisiae genome that are re-replicated as well as sites of pre-RC formation during re-replication. Only a fraction of the genome is re-replicated by a subset of origins, some of which are capable of multiple reinitiation events. Translocation experiments demonstrate that origin-proximal sequences are sufficient to predispose an origin to re-replication. Origins that reinitiate are largely limited to those that can recruit Mcm2-7 under re-replicating conditions; however, the formation of a pre-RC is not sufficient for reinitiation. Our findings allow us to categorize origins with respect to their propensity to reinitiate and demonstrate that pre-RC formation is not the only target for the mechanisms that prevent genomic re-replication.
Figures
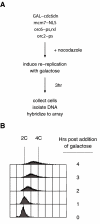
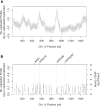

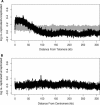
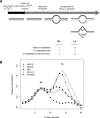
References
-
- Aparicio, O. M., Weinstein, D. M., and Bell, S. P. (1997). Components and dynamics of DNA replication complexes in S. cerevisiae: redistribution of MCM proteins and Cdc45p during S phase. Cell 91, 59-69. - PubMed
-
- Bell, S. P., and Dutta, A. (2002). DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 333-374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

