Protein kinase Czeta mediates insulin-induced glucose transport through actin remodeling in L6 muscle cells
- PMID: 16525020
- PMCID: PMC1446104
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-10-0969
Protein kinase Czeta mediates insulin-induced glucose transport through actin remodeling in L6 muscle cells
Abstract
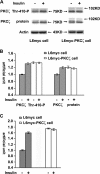
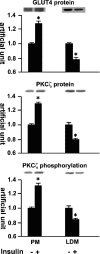
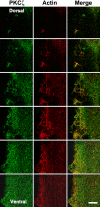
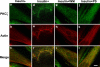
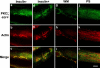
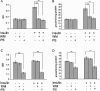
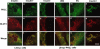
Protein kinase C (PKC) zeta has been implicated in insulin-induced glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cell, although the underlying mechanism remains unknown. In this study, we investigated the effect of PKCzeta on actin remodeling and glucose transport in differentiated rat L6 muscle cells expressing myc-tagged glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4). On insulin stimulation, PKCzeta translocated from low-density microsomes to plasma membrane accompanied by increase in GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake. Z-scan confocal microscopy revealed a spatial colocalization of relocated PKCzeta with the small GTPase Rac-1, actin, and GLUT4 after insulin stimulation. The insulin-mediated colocalization, PKCzeta distribution, GLUT4 translocation, and glucose uptake were inhibited by wortmannin and cell-permeable PKCzeta pseudosubstrate peptide. In stable transfected cells, overexpression of PKCzeta caused an insulin-like effect on actin remodeling accompanied by a 2.1-fold increase in GLUT4 translocation and 1.7-fold increase in glucose uptake in the absence of insulin. The effects of PKCzeta overexpression were abolished by cell-permeable PKCzeta pseudosubstrate peptide, but not wortmannin. Transient transfection of constitutively active Rac-1 recruited PKCzeta to new structures resembling actin remodeling, whereas dominant negative Rac-1 prevented the insulin-mediated PKCzeta translocation. Together, these results suggest that PKCzeta mediates insulin effect on glucose transport through actin remodeling in muscle cells.
Figures
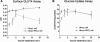
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C-zeta regulation of GLUT4 translocation through actin remodeling in CHO cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2007 Aug;85(8):851-61. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0232-z. Epub 2007 Jul 10. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17619838
-
Identification of 80K-H as a protein involved in GLUT4 vesicle trafficking.Biochem J. 2005 Jun 15;388(Pt 3):785-93. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041845. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15707389 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acids inhibit insulin-mediated glucose transport associated with actin remodeling in rat L6 muscle cells.Acta Diabetol. 2010 Dec;47(4):331-9. doi: 10.1007/s00592-010-0225-1. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Acta Diabetol. 2010. PMID: 20848165
-
Rac1 signalling towards GLUT4/glucose uptake in skeletal muscle.Cell Signal. 2011 Oct;23(10):1546-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.05.022. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21683139 Review.
-
Protein kinase Czeta and glucose uptake.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2006 Jul;71(7):701-6. doi: 10.1134/s0006297906070017. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2006. PMID: 16903823 Review.
Cited by
-
Rac1 signaling is required for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and is dysregulated in insulin-resistant murine and human skeletal muscle.Diabetes. 2013 Jun;62(6):1865-75. doi: 10.2337/db12-1148. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23423567 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protein kinase C-zeta regulation of GLUT4 translocation through actin remodeling in CHO cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2007 Aug;85(8):851-61. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0232-z. Epub 2007 Jul 10. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17619838
-
Metabolic functions of atypical protein kinase C: "good" and "bad" as defined by nutritional status.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Mar;298(3):E385-94. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00608.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 8. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 19996389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid oversupply induces CD36 sarcolemmal translocation via dual modulation of PKCζ and TBC1D1: an early event prior to insulin resistance.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 1;10(3):1332-1354. doi: 10.7150/thno.40021. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 31938068 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral delivery of a ROCK inhibitor improves learning and working memory.Behav Neurosci. 2009 Feb;123(1):218-23. doi: 10.1037/a0014260. Behav Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19170447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandyopadhyay, G., Sajan, M. P., Kanoh, Y., Standaert, M. L., Quon, M. J., Lea-Currie, R., Sen, A., and Farese, R. V. (2002). Protein kinase C-zeta mediates insulin effects on glucose transport in cultured preadipocyte-derived human adipocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 716-723. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay, G., Standaert, M. L., Galloway, L., Moscat, J., and Farese, R. V. (1997a). Evidence for involvement of protein kinase C-zeta and noninvolvement of diacylglycerol-sensitive PKCs in insulin-stimulated glucose transport in L6 myotubes. Endocrinology 138, 4721-4731. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay, G., Standaert, M. L., Kikkawa, U., Ono, Y., Moscat, J., and Farese, R. V. (1999). Effects of transiently expressed atypical (zeta, lambda), conventional (alpha, beta) and novel (delta, epsilon) protein kinase C isoforms on insulin-stimulated translocation of epitope-tagged GLUT4 glucose transporters in rat adipocytes: specific interchangeable effects of protein kinases C-zeta and C-lambda. Biochem. J. 337, 461-470. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay, G., Standaert, M. L., Zhao, L., Yu, B., Avignon, A., Galloway, L., Karnam, P., Moscat, J., and Farese, R. V. (1997b). Activation of protein kinase C (alpha, beta, and zeta) by insulin in 3T3/L1 cells. Transfection studies suggest a role for protein kinase C-zeta in glucose transport. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 2551-2558. - PubMed
-
- Beeson, M., et al. (2003). Activation of protein kinase C-zeta by insulin and phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-(PO4)3 is defective in muscle in type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance: amelioration by rosiglitazone and exercise. Diabetes 52, 1926-1934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

