A common ankyrin-G-based mechanism retains KCNQ and NaV channels at electrically active domains of the axon
- PMID: 16525039
- PMCID: PMC6675151
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4314-05.2006
A common ankyrin-G-based mechanism retains KCNQ and NaV channels at electrically active domains of the axon
Abstract
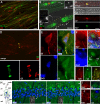
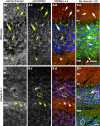
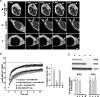
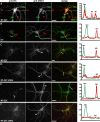
KCNQ (KV7) potassium channels underlie subthreshold M-currents that stabilize the neuronal resting potential and prevent repetitive firing of action potentials. Here, antibodies against four different KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 polypeptide epitopes show these subunits concentrated at the axonal initial segment (AIS) and node of Ranvier. AIS concentration of KCNQ2 and KCNQ3, like that of voltage-gated sodium (NaV) channels, is abolished in ankyrin-G knock-out mice. A short motif, common to KCNQ2 and KCNQ3, mediates both in vivo ankyrin-G interaction and retention of the subunits at the AIS. This KCNQ2/KCNQ3 motif is nearly identical to the sequence on NaV alpha subunits that serves these functions. All identified NaV and KCNQ genes of worms, insects, and molluscs lack the ankyrin-G binding motif. In contrast, vertebrate orthologs of NaV alpha subunits, KCNQ2, and KCNQ3 (including from bony fish, birds, and mammals) all possess the motif. Thus, concerted ankyrin-G interaction with KCNQ and NaV channels appears to have arisen through convergent molecular evolution, after the division between invertebrate and vertebrate lineages, but before the appearance of the last common jawed vertebrate ancestor. This includes the historical period when myelin also evolved.
Figures




References
-
- Adelman JP, Bond CT, Pessia M, Maylie J (1995). Episodic ataxia results from voltage-dependent potassium channels with altered functions. Neuron 15:1449–1454. - PubMed
-
- Anderson WA, Flumerfelt BA (1984). Time course of mossy fiber degeneration following pontine ablation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 227:401–413. - PubMed
-
- Bennett V, Baines AJ (2001). Spectrin and ankyrin-based pathways: metazoan inventions for integrating cells into tissues. Physiol Rev 81:1353–1392. - PubMed
-
- Biervert C, Schroeder BC, Kubisch C, Berkovic SF, Propping P, Jentsch TJ, Steinlein OK (1998). A potassium channel mutation in neonatal human epilepsy. Science 279:403–406. - PubMed
-
- Brown D (1988). M-currents: an update. Trends Neurosci 11:294–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
