siRNA-mediated simultaneous downregulation of uPA and its receptor inhibits angiogenesis and invasiveness triggering apoptosis in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 16525631
- PMCID: PMC1398074
siRNA-mediated simultaneous downregulation of uPA and its receptor inhibits angiogenesis and invasiveness triggering apoptosis in breast cancer cells
Abstract
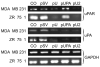
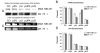
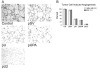
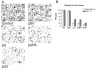
A wide variety of tumor cells exhibit overexpression of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) and its receptor (uPAR). In breast cancer, expression of uPA and uPAR is essential for tumor cell invasion and metastasis. It is also known that uPA binds to uPAR and activates the RAS extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway. In our study, small interfering RNA (siRNA) was introduced to downregulate the expression of uPA and uPAR in two breast cancer cell lines (MDA MB 231 and ZR 75 1). uPA and uPAR were downregulated individually using single constructs, and in combination using a bicistronic construct driven by a CMV promoter in a pcDNA-3 mammalian expression vector. Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and Western blot analyses indicated downregulation at both the mRNA and protein levels. In vitro angiogenesis studies using conditioned medium in HMEC-1 cells indicated a decrease in the angiogenic potential of conditioned media from treated cells when compared to the controls. This decrease in angiogenic potential was remarkably higher with the bicistronic construct. Similarly, the invasive potential of these cells decreased dramatically when treated with the bicistronic construct, thereby suggesting a synergistic effect from the downregulation of both uPA and uPAR. Furthermore, when uPA and uPAR were downregulated simultaneously, the apoptotic cascade was triggered as indicated by the upregulation of both initiator and effector caspases as well as other pro-apoptotic molecules. A mitochondrial permeability assay and FACS analysis revealed an increase in apoptotic cells in the uPA/uPAR treatment as compared to the other treatments. This overexpression of pro-apoptotic caspases in relation to the RNAi-induced downregulation of uPA and uPAR clearly suggests the involvement of the uPA-uPAR system in cell survival and proliferation in addition to their role in tumor progression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated urokinase-specific surface receptor expression is maintained through its interaction with urokinase plasminogen activator.Mol Carcinog. 2007 Mar;46(3):165-75. doi: 10.1002/mc.20249. Mol Carcinog. 2007. PMID: 17186542
-
RNAi-mediated downregulation of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and matrix metalloprotease-9 in human breast cancer cells results in decreased tumor invasion, angiogenesis and growth.Int J Cancer. 2007 Nov 15;121(10):2307-16. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22962. Int J Cancer. 2007. Retraction in: Int J Cancer. 2021 Feb 26. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33520. PMID: 17657740 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Calcitonin inhibits invasion of breast cancer cells: involvement of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and uPA receptor.Int J Oncol. 2006 Apr;28(4):807-14. Int J Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16525628
-
Inhibition of the tumor-associated urokinase-type plasminogen activation system: effects of high-level synthesis of soluble urokinase receptor in ovarian and breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2003;162:43-63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59349-9_4. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12790320 Review.
-
Regulation and role of urokinase plasminogen activator in vascular remodelling.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1996 Sep;23(9):759-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1996.tb01177.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8911711 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of miR-193a and sorafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer. 2013 Dec 13;12:162. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-162. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24330766 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor by Docosahexaenoic Acid Mediated by Heme Oxygenase-1 in 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate-Induced Human Endothelial Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 26;11:577302. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.577302. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33381031 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine-kinase inhibition results in EGFR clustering at focal adhesions and consequent exocytosis in uPAR down-regulated cells of head and neck cancers.Mol Cancer. 2008 Jun 3;7:47. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-47. Mol Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18519000 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen activator urokinase expression reveals TRAIL responsiveness and supports fractional survival of cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jan 30;5(1):e1043. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.5. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24481457 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Role of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Its Receptor (uPAR): Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Applications.Front Oncol. 2018 Feb 12;8:24. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00024. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29484286 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blasi F. uPA, uPAR, PAI-1: key intersection of proteolytic, adhesive and chemotactic highways? Immunol. Today. 1997;18:415–417. - PubMed
-
- Leirisalo-Repo M.The present knowledge of the inflammatory process and the inflammatory mediators Pharmacol Toxicol 199475Suppl 21–3.1-3 - PubMed
-
- Camussi G, Montrucchio G, Lupia E, Soldi R, Comoglio PM, Bussolino F. Angiogenesis induced in vivo by hepatocyte growth factor is mediated by platelet-activating factor synthesis from macrophages. J Immunol. 1997;158:1302–1309. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Ingbar DH, Henke CA. Integrin mediation of type II cell adherence to provisional matrix proteins. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:L277–L286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

