Identification and characterization of noncalcemic, tissue-selective, nonsecosteroidal vitamin D receptor modulators
- PMID: 16528410
- PMCID: PMC1395481
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25901
Identification and characterization of noncalcemic, tissue-selective, nonsecosteroidal vitamin D receptor modulators
Abstract
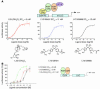
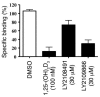
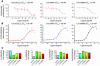
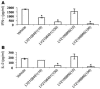
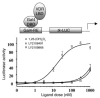
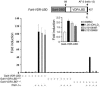
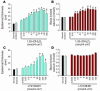
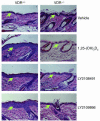
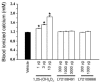
Vitamin D receptor (VDR) ligands are therapeutic agents for the treatment of psoriasis, osteoporosis, and secondary hyperparathyroidism. VDR ligands also show immense potential as therapeutic agents for autoimmune diseases and cancers of skin, prostate, colon, and breast as well as leukemia. However, the major side effect of VDR ligands that limits their expanded use and clinical development is hypercalcemia that develops as a result of the action of these compounds mainly on intestine. In order to discover VDR ligands with less hypercalcemia liability, we sought to identify tissue-selective VDR modulators (VDRMs) that act as agonists in some cell types and lack activity in others. Here, we describe LY2108491 and LY2109866 as nonsecosteroidal VDRMs that function as potent agonists in keratinocytes, osteoblasts, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells but show poor activity in intestinal cells. Finally, these nonsecosteroidal VDRMs were less calcemic in vivo, and LY2108491 exhibited more than 270-fold improved therapeutic index over the naturally occurring VDR ligand 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25-(OH)2D3] in an in vivo preclinical surrogate model of psoriasis.
Figures


Comment in
- J Clin Invest. 116:872.
References
-
- Bettoun D.J., et al. Retinoid X receptor is a nonsilent major contributor to vitamin D receptor-mediated transcriptional activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003;17:2320–2328. - PubMed
-
- Rachez C., Freedman L.P. Mechanisms of gene regulation by vitamin D(3) receptor: a network of coactivator interactions. Gene. 2000;246:9–21. - PubMed
-
- Holick M.F. Noncalcemic actions of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and clinical applications. Bone. 1995;17(Suppl. 2):107S–111S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

