CD137-mediated immunotherapy for allergic asthma
- PMID: 16528411
- PMCID: PMC1395480
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23792
CD137-mediated immunotherapy for allergic asthma
Abstract
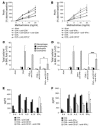
The prevalence of asthma continues to increase. Asthma is caused by a Th2 cell-driven immune response. Its optimal treatment remains a challenge, and a sufficient immunotherapeutic approach to treating asthma has yet to be found. Using a murine asthma model, we show that a single injection of an anti-CD137 (4-1BB) mAb prevents the development of airway hyperreactivity, eosinophilic airway inflammation, excessive mucus production, and elevated IgE during the observation period of 7 weeks. Most importantly, even established disease is completely reversed by anti-CD137 mAb administration. The protection is associated with markedly reduced Th2 cytokine production and increased secretion of the Th1 cytokine IFN-gamma. While B lymphocytes are partly depleted, the number of CD8+ T cells is increased. Blockade of IFN-gamma and depletion of CD8+ T cells during treatment with anti-CD137 mAb reduces in part but does not abrogate the protective effect of CD137 mAb. In contrast, CD137 mAb-mediated CD4+ T cell anergy is critical for the observed effects, since transfer of CD4+ T cells from CD137 mAb-treated mice conveyed protection. These data demonstrate, for the first time to our knowledge, the capacity of anti-CD137 mAb to ameliorate allergic asthma, and they indicate CD137 as a possible target for therapeutic intervention in this disease.
Figures

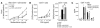
Similar articles
-
4-1 BB stimulation inhibits allergen-specific immunoglobulin E production and airway hyper-reactivity but partially suppresses bronchial eosinophilic inflammation in a mouse asthma model.Clin Exp Allergy. 2006 Mar;36(3):377-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02445.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. PMID: 16499650
-
CD137 ligand prevents the development of T-helper type 2 cell-mediated allergic asthma by interferon-gamma-producing CD8+ T cells.Clin Exp Allergy. 2007 Sep;37(9):1374-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2007.02785.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007. PMID: 17845419
-
Inhibition of Th2-mediated allergic airway inflammatory disease by CD137 costimulation.J Immunol. 2006 Jul 15;177(2):814-21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.814. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16818735
-
Immunotherapy with agonistic anti-CD137: two sides of a coin.Cell Mol Immunol. 2004 Feb;1(1):31-6. Cell Mol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 16212918 Review.
-
T-cell costimulatory molecules: optimal targets for the treatment of allergic airway disease with monoclonal antibodies.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005 Oct;116(4):906-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.07.005. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16210068 Review.
Cited by
-
Reverse signaling through the costimulatory ligand CD137L in epithelial cells is essential for natural killer cell-mediated acute tissue inflammation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 3;109(1):E13-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112256109. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22160719 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention with costimulatory pathways as a therapeutic approach for graft-versus-host disease.Exp Mol Med. 2010 Oct 31;42(10):675-83. doi: 10.3858/emm.2010.42.10.071. Exp Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20820112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAR-NKT Cells in Asthma: Use of NKT as a Promising Cell for CAR Therapy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024 Jun;66(3):328-362. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-08998-0. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38995478 Review.
-
Anti-Asthma Simplified Herbal Medicine Intervention-induced long-lasting tolerance to allergen exposure in an asthma model is interferon-γ, but not transforming growth factor-β dependent.Clin Exp Allergy. 2010 Nov;40(11):1678-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03545.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010. PMID: 20573156 Free PMC article.
-
Hu.4-1BB-Fc fusion protein inhibits allergic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma.Korean J Pediatr. 2011 Sep;54(9):373-9. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2011.54.9.373. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Korean J Pediatr. 2011. PMID: 22232630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Umetsu D.T., McIntire J.J., Akbari O., Macaubas C., DeKruyff R.H. Asthma: an epidemic of dysregulated immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:715–720. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz J.C., Zhang X., Nathenson S.G., Almo S.C. Structural mechanisms of costimulation. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:427–434. - PubMed
-
- Harding F.A., McArthur J.G., Gross J.A., Raulet D.H., Allison J.P. CD28-mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature. 1992;356:607–609. - PubMed
-
- Rudd C.E., Schneider H. Unifying concepts in CD28, ICOS and CTLA4 co-receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:544–556. - PubMed
-
- Coyle A.J., Gutierrez-Ramos J.C. The role of ICOS and other costimulatory molecules in allergy and asthma. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 2004;25:349–359. - PubMed

