Selective elimination of human regulatory T lymphocytes in vitro with the recombinant immunotoxin LMB-2
- PMID: 16531821
- PMCID: PMC1473974
- DOI: 10.1097/01.cji.0000187959.45803.0c
Selective elimination of human regulatory T lymphocytes in vitro with the recombinant immunotoxin LMB-2
Abstract
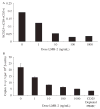
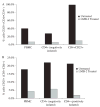
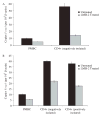
CD4(+)CD25(+) T-regulatory cells (T(reg)) can inhibit the proliferation and cytokine secretion of CD4(+)CD25(-) helper T cells in mice and humans. In murine tumor models, the presence of these T(reg) cells can inhibit the antitumor effectiveness of T-cell transfer and active immunization approaches. We have thus initiated efforts to eliminate T(reg) cells selectively from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to potentially bolster antitumor responses. LMB-2 is a recombinant immunotoxin that is a fusion of a single-chain Fv fragment of the anti-Tac anti-CD25 monoclonal antibody to a truncated form of the bacterial Pseudomonas exotoxin A. In vitro incubation of human PBMCs with LMB-2 reduced the levels of CD4(+)CD25(+) and Foxp3-expressing cells without impairing the function of the remaining lymphocytes. The short in vivo half-life of LMB-2 makes it an attractive candidate for reducing human T(reg) cells in vivo before the administration of cancer vaccine or cell transfer immunotherapy approaches.
Figures

References
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:531–562. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:345–352. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, et al. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet. 2001;27:20–21. - PubMed
-
- Wang HY, Lee DA, Peng G, et al. Tumor-specific human CD4+ regulatory T cells and their ligands: implications for immunotherapy. Immunity. 2004;20:107–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

