Regulation of IL-1-induced selective IL-6 release from human mast cells and inhibition by quercetin
- PMID: 16532021
- PMCID: PMC1617055
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706695
Regulation of IL-1-induced selective IL-6 release from human mast cells and inhibition by quercetin
Abstract
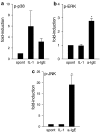
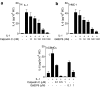
Mast cells are involved in allergic reactions, but also in innate immunity and inflammation. Crosslinkage of mast cell Fc immunoglobulin E receptors (FcvarepsilonRI) by multivalent antigen triggers secretion of granule-stored mediators, as well as de novo synthesis of cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-6. We showed recently that the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1 stimulates human leukemic mast cells (HMC-1) and human umbilical cord blood-derived cultured mast cells (hCBMCs) to release newly synthesized IL-6 without tryptase in the absence of degranulation. Here, we investigated several signal-transduction pathways activated by IL-1 leading to IL-6 production by HMC-1 and hCBMCs. We also investigated the effect of the flavonol quercetin that was recently shown to strongly inhibit IL-6 secretion in response to allergic stimulation from hCBMCs.IL-1 stimulated p38, but did not activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) or c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK); it also did not activate protein kinase C (PKC) isozymes alpha, beta, mu and zeta, except for PKC-theta, which was phosphorylated. The p38 inhibitor SB203580 and the PKC inhibitors Calphostin C and Gö6976 completely inhibited IL-1-induced IL-6 production. Quercetin 1-100 microM inhibited IL-1-induced IL-6 secretion, p38 and PKC-theta phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. These results indicate that IL-1-stimulated IL-6 production from human mast cells is regulated by biochemical pathways distinct from IgE-induced degranulation and that quercetin can block both IL-6 secretion and two key signal transduction steps involved.
Figures
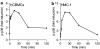
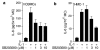


Similar articles
-
Flavonols inhibit proinflammatory mediator release, intracellular calcium ion levels and protein kinase C theta phosphorylation in human mast cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Aug;145(7):934-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706246. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15912140 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin-releasing hormone induces vascular endothelial growth factor release from human mast cells via the cAMP/protein kinase A/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;69(3):998-1006. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.019539. Epub 2005 Dec 6. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16332989
-
Akt cross-links IL-4 priming, stem cell factor signaling, and IgE-dependent activation in mature human mast cells.Mol Immunol. 2011 Jan;48(4):546-52. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.10.010. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21106245
-
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases are involved in interleukin-1 (IL-1)-induced IL-6 synthesis in osteoblasts: modulation not of p38 MAP kinase, but of p42/p44 MAP kinase by IL-1-activated protein kinase C.Endocrinology. 1999 Nov;140(11):5120-5. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.11.7123. Endocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10537140
-
Signal pathway of cytokines produced by reactive oxygen species generated from phorbol myristate acetate-stimulated HMC-1 cells.Scand J Immunol. 2005 Jul;62(1):25-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2005.01636.x. Scand J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16091123
Cited by
-
Induction of cellular and molecular immunomodulatory pathways by vitamin A and flavonoids.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(10):1411-28. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2015.1066331. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26185959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Role of Moesin in Regulating Mast Cell Secretion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12081. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512081. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of polyphenols on mast cells with special emphasis on the effect of quercetin and luteolin.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2018;43(4):476-481. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2018.81347. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30799996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-sensitive effects of quercetin on rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cell responsiveness and intracellular signaling.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 24;20(2):e0319103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319103. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39992972 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive effects of quercetin against foot-and-mouth disease virus in vitro and in vivo by inducing type I interferon.Front Microbiol. 2023 May 12;14:1121830. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1121830. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37250022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BLANK U., RIVERA J. The ins and outs of IgE-dependent mast-cell exocytosis. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:266–273. - PubMed
-
- BUTTERFIELD J.H., WEILER D., DEWALD G., GLEICH G.J. Establishment of an immature mast cell line from a patient with mast cell leukemia. Leuk. Res. 1988;12:345–355. - PubMed
-
- CHANG E.Y., SZALLASI Z., ACS P., RAIZADA V., WOLFE P.C., FEWTRELL C., BLUMBERG P.M., RIVERA J. Functional effects of overexpression of protein kinase C-alpha, -beta, -delta, -epsilon, and -eta in the mast cell line RBL-2H3. J. Immunol. 1997;159:2624–2632. - PubMed
-
- CHO S.Y., PARK S.J., KWON M.J., JEONG T.S., BOK S.H., CHOI W.Y., JEONG W.I., RYU S.Y., DO S.H., LEE C.S., SONG J.C., JEONG K.S. Quercetin suppresses proinflammatory cytokines production through MAP kinases and NF-kappaB pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003;243:153–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

