Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces HIF-1 activation in human monocytes via p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB
- PMID: 16533170
- PMCID: PMC1482811
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051839
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces HIF-1 activation in human monocytes via p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB
Abstract
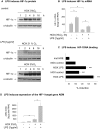
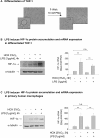
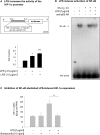
Inflammatory mediators activate the transcriptional complex HIF-1 (hypoxia-inducible factor-1), the key regulator of hypoxia-induced gene expression. Here we report that bacterial LPS (lipopolysaccharide) induces HIF-1alpha mRNA expression and HIF-1alpha protein accumulation in human monocytes as well as in non-differentiated and differentiated cells of the human monocytic cell line THP-1 under normoxic conditions. LPS and hypoxia synergistically activated HIF-1. Whereas LPS increased HIF-1alpha mRNA expression through activation of a NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB) site in the promoter of the HIF-1alpha gene, hypoxia post-translationally stabilized HIF-1alpha protein. HIF-1alpha activation was followed by increased expression of the HIF-1 target gene encoding ADM (adrenomedullin). Knocking down HIF-1alpha by RNA interference significantly decreased ADM expression, which underlines the importance of HIF-1 for the LPS-induced ADM expression in normoxia. Simultaneously with HIF-1 activation, an increase in p44/42 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) phosphorylation was observed after incubation with LPS. In cells pretreated with the p44/42 MAPK inhibitor PD 98059 or with RNAi (interfering RNA) directed against p44/42 MAPK, LPS-induced HIF-1alpha accumulation and ADM expression were significantly decreased. From these results we conclude that LPS critically involves the p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathway in the activation of HIF-1, which is an important transcription factor for LPS-induced ADM expression.
Figures
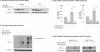


Similar articles
-
p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1.J Biol Chem. 1999 Nov 12;274(46):32631-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.46.32631. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10551817
-
[Hypoxia/reoxygenation and lipopolysaccharide induced nuclear factor-ΚB and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cell injury and the interventional effect of emodin].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Jun;26(6):409-14. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.06.009. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 24912640 Chinese.
-
A(1) and A(3) adenosine receptors inhibit LPS-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1 accumulation in murine astrocytes.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Oct;76:157-70. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23969284
-
Chronic and Cycling Hypoxia: Drivers of Cancer Chronic Inflammation through HIF-1 and NF-κB Activation: A Review of the Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10701. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910701. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic evolutionary roots of the macrophage immune response in amoeba-bacteria interactions: The conserved role of hypoxia-induced Factor and AMP kinase.Acta Biochim Pol. 2021 Aug 10;68(3):457-476. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5683. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021. PMID: 34374500 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein in human cytomegalovirus-induced hyperpermeability of human endothelial cells.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Aug;16(2):1295-1303. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6332. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30112061 Free PMC article.
-
Placenta growth factor-induced early growth response 1 (Egr-1) regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) in endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 2;285(27):20570-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.119495. Epub 2010 May 6. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20448047 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between hypoxic cellular micro-environment and the immune system: a potential therapeutic target for infectious diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 31;14:1224102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1224102. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600803 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological Characteristics of the Thymus and Spleen and the Subpopulation Composition of Lymphocytes in Peripheral Blood during Systemic Inflammatory Response in Male Rats with Different Resistance to Hypoxia.Int J Inflam. 2019 Apr 1;2019:7584685. doi: 10.1155/2019/7584685. eCollection 2019. Int J Inflam. 2019. PMID: 31057785 Free PMC article.
-
hERG1 channels modulate integrin signaling to trigger angiogenesis and tumor progression in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2013 Nov 25;3:3308. doi: 10.1038/srep03308. Sci Rep. 2013. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 28;15(1):3550. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87746-6. PMID: 24270902 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Masson N., Ratcliffe P. J. HIF prolyl and asparaginyl hydroxylases in the biological response to intracellular O2 levels. J. Cell. Sci. 2003;116:3041–3049. - PubMed
-
- Jaakkola P., Mole D. R., Tian Y. M., Wilson M. I., Gielbert J., Gaskell S. J., Kriegsheim A., Hebestreit H. F., Mukherji M., Schofield C. J., et al. Targeting of HIF-α to the von Hippel–Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292:468–472. - PubMed
-
- Ivan M., Kondo K., Yang H., Kim W., Valiando J., Ohh M., Salic A., Asara J. M., Lane W. S., Kaelin W. G., Jr HIFα targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science. 2001;292:464–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

