Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces HIF-1 activation in human monocytes via p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB
- PMID: 16533170
- PMCID: PMC1482811
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051839
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces HIF-1 activation in human monocytes via p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB
Abstract
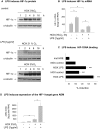
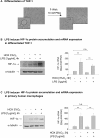
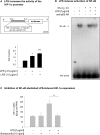
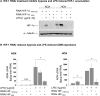
Inflammatory mediators activate the transcriptional complex HIF-1 (hypoxia-inducible factor-1), the key regulator of hypoxia-induced gene expression. Here we report that bacterial LPS (lipopolysaccharide) induces HIF-1alpha mRNA expression and HIF-1alpha protein accumulation in human monocytes as well as in non-differentiated and differentiated cells of the human monocytic cell line THP-1 under normoxic conditions. LPS and hypoxia synergistically activated HIF-1. Whereas LPS increased HIF-1alpha mRNA expression through activation of a NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB) site in the promoter of the HIF-1alpha gene, hypoxia post-translationally stabilized HIF-1alpha protein. HIF-1alpha activation was followed by increased expression of the HIF-1 target gene encoding ADM (adrenomedullin). Knocking down HIF-1alpha by RNA interference significantly decreased ADM expression, which underlines the importance of HIF-1 for the LPS-induced ADM expression in normoxia. Simultaneously with HIF-1 activation, an increase in p44/42 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) phosphorylation was observed after incubation with LPS. In cells pretreated with the p44/42 MAPK inhibitor PD 98059 or with RNAi (interfering RNA) directed against p44/42 MAPK, LPS-induced HIF-1alpha accumulation and ADM expression were significantly decreased. From these results we conclude that LPS critically involves the p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathway in the activation of HIF-1, which is an important transcription factor for LPS-induced ADM expression.
Figures
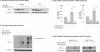


References
-
- Masson N., Ratcliffe P. J. HIF prolyl and asparaginyl hydroxylases in the biological response to intracellular O2 levels. J. Cell. Sci. 2003;116:3041–3049. - PubMed
-
- Jaakkola P., Mole D. R., Tian Y. M., Wilson M. I., Gielbert J., Gaskell S. J., Kriegsheim A., Hebestreit H. F., Mukherji M., Schofield C. J., et al. Targeting of HIF-α to the von Hippel–Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292:468–472. - PubMed
-
- Ivan M., Kondo K., Yang H., Kim W., Valiando J., Ohh M., Salic A., Asara J. M., Lane W. S., Kaelin W. G., Jr HIFα targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science. 2001;292:464–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

