The effects of a novel MEK inhibitor PD184161 on MEK-ERK signaling and growth in human liver cancer
- PMID: 16533420
- PMCID: PMC1601146
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.05373
The effects of a novel MEK inhibitor PD184161 on MEK-ERK signaling and growth in human liver cancer
Abstract
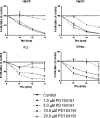
The MEK-ERK growth signaling pathway is important in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). To evaluate the targeting of this pathway in HCC, we characterized a novel, orally-active MEK inhibitor, PD184161, using human HCC cells (HepG2, Hep3B, PLC, and SKHep) and in vivo human tumor xenografts. PD184161 inhibited MEK activity (IC50 = 10-100 nM) in a time- and concentration-dependent manner more effectively than PD098059 or U0126. PD184161 inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis at concentrations of > or = 1.0 microM in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. In vivo, tumor xenograft P-ERK levels were significantly reduced 3 to 12 hours after an oral dose of PD184161 (P < .05). Contrarily, tumor xenograft P-ERK levels following long-term (24 days) daily dosing of PD184161 were refractory to this signaling effect. PD184161 significantly suppressed tumor engraftment and initial growth (P < .0001); however, established tumors were not significantly affected. In conclusion, PD184161 has antitumor effects in HCC in vitro and in vivo that appear to correlate with suppression of MEK activity. These studies demonstrate that PD184161 is unable to suppress MEK activity in HCC xenografts in the long term. Thus, we speculate that the degree of success of MEK targeted treatment in HCC and other cancers may, in part, depend on the discovery of mechanisms governing MEK inhibitor signaling resistance.
Figures

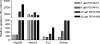
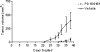
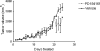
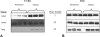
Similar articles
-
The effect of doxorubicin on MEK-ERK signaling predicts its efficacy in HCC.J Surg Res. 2008 Dec;150(2):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2008.01.029. Epub 2008 Mar 3. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 18468633
-
Resistance to mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors correlates with up-regulation of the MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Jun;329(3):1063-70. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.147306. Epub 2009 Mar 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19258520
-
Multiple anticancer effects of blocking MEK-ERK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Am Coll Surg. 2004 Mar;198(3):410-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2003.10.004. J Am Coll Surg. 2004. PMID: 14992744
-
Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5.Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 15;66(24):11851-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1377. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17178882
-
Ethanol-TGFalpha-MEK signaling promotes growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma.J Surg Res. 2009 Jun 15;154(2):187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2008.11.836. Epub 2008 Dec 13. J Surg Res. 2009. PMID: 19321179 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Strategies for Improving Photodynamic Therapy Through Pharmacological Modulation of the Immediate Early Stress Response.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2451:405-480. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2099-1_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35505025 Review.
-
Effects and mechanisms of silibinin on human hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts in nude mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Apr 28;15(16):1943-50. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1943. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19399925 Free PMC article.
-
Proteinase-activated receptor 2-mediated calcium signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011 Jun;137(6):965-73. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0961-1. Epub 2010 Dec 2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21125404 Free PMC article.
-
Current Development Status of MEK Inhibitors.Molecules. 2017 Sep 26;22(10):1551. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101551. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28954413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neoplasia: the second decade.Neoplasia. 2008 Dec;10(12):1314-24. doi: 10.1593/neo.81372. Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 19048110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosch FX, Ribes J, Cleries R, Diaz M. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9:191–211. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–1917. - PubMed
-
- Olthoff KM. Surgical options for hepatocellular carcinoma: resection and transplantation. Liver Transplant Surg. 1998;4:S98–S104. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM. Updated treatment approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:225–235. - PubMed
-
- Coleman WB. Mechanisms of human hepatocarcinogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 2003;3:573–588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
