Folding, misfolding, and amyloid protofibril formation of WW domain FBP28
- PMID: 16533840
- PMCID: PMC1459504
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.076406
Folding, misfolding, and amyloid protofibril formation of WW domain FBP28
Abstract
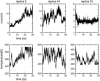
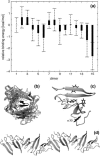
We study the folding mechanism of a triple beta-strand WW domain from the Formin binding protein 28 (FBP28) at atomic resolution with explicit water model using replica exchange molecular dynamics computer simulations. Extended sampling over a wide range of temperatures to obtain the free energy, enthalpy, and entropy surfaces as a function of structural coordinates has been performed. Simulations were started from different configurations covering the folded and unfolded states. In the free energy landscape a transition state is identified and its structures and -values are compared with experimental data from a homologous protein, the prolyl-isomerase Pin1 WW domain. A stable intermediate state is found to accumulate during the simulation characterized by the carboxyl-terminal beta-strand 3 having misregistered hydrogen bonds and where the structural heterogeneity is due to nonnative turn II formation. Furthermore, the aggregation behavior of the FBP28 WW domain may be related to one such misfolded structure, which has a much lower free energy of dimer formation than that of the native dimer. Based on the misfolded dimer, aggregation to form protofibril structure is discussed.
Figures






References
-
- Fersht, A. 1998. Enzyme Structure, Mechanism & Protein Folding, 3rd ed. W. H. Freeman, New York.
-
- Kubelka, J., J. Hofrichter, and W. A. Eaton. 2004. The protein folding ‘speed limit’. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 14:76–88. - PubMed
-
- Zhou, Y., and M. Karplus. 1999. Interpreting the folding kinetics of helical proteins. Nature. 401:400–403. - PubMed
-
- Munoz, V., P. A. Thompson, J. Hofrichter, and W. A. Eaton. 1997. Folding dynamics and mechanism of beta-hairpin fromation. Nature. 390:196–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

