Development of contrast agents targeted to macrophage scavenger receptors for MRI of vascular inflammation
- PMID: 16536488
- PMCID: PMC2556229
- DOI: 10.1021/bc060018k
Development of contrast agents targeted to macrophage scavenger receptors for MRI of vascular inflammation
Abstract
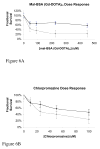
Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of death in the U.S. Because there is a potential to prevent coronary and arterial disease through early diagnosis, there is a need for methods to image arteries in the subclinical stage as well as clinical stage using various noninvasive techniques, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). We describe a development of a novel MRI contrast agent targeted to plaques that will allow imaging of lesion formation. The contrast agent is directed to macrophages, one of the earliest components of developing plaques. Macrophages are labeled through the macrophage scavenger receptor A, a macrophage specific cell surface protein, using an MRI contrast agent derived from scavenger receptor ligands. We have synthesized and characterized these contrast agents with a range of relaxivities. In vitro studies show that the targeted contrast agent accumulates in macrophages, and solution studies indicate that micromolar concentrations are sufficient to produce contrast in an MR image. Cell toxicity and initial biodistribution studies indicate low toxicity, no detectable retention in normal blood vessels, and rapid clearance from blood. The promising performance of this contrast agent targeted toward vascular inflammation opens doors to tracking of other inflammatory diseases such as tumor immunotherapy and transplant acceptance using MRI.
Figures







References
-
- Desai MY, Bluemke DA. Atherosclerosis imaging using MR imaging: current and emerging applications. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2005;13:171–80. vii. - PubMed
-
- Rogers WJ, Prichard JW, Hu YL, Olson PR, Benckart DH, Kramer CM, Vido DA, Reichek N. Characterization of signal properties in atherosclerotic plaque components by intravascular MRI. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1824–30. - PubMed
-
- Fayad ZA. MR imaging for the noninvasive assessment of atherothrombotic plaques. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2003;11:101–13. - PubMed
-
- Choudhury RP, Fuster V, Fayad ZA. Molecular, cellular and functional imaging of atherothrombosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:913–25. - PubMed
-
- Ruygrok P, Webster M, deValk V, vanEs G, Ormiston J, Morel M, Serruys P. Clinical and angiographic factors associated with asymptomatic restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2001;104:2289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

