Global identification of noncoding RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by modulating an essential RNA processing pathway
- PMID: 16537507
- PMCID: PMC1389707
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507669103
Global identification of noncoding RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by modulating an essential RNA processing pathway
Abstract
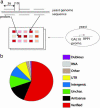
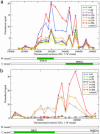
Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) perform essential cellular tasks and play key regulatory roles in all organisms. Although several new ncRNAs in yeast were recently discovered by individual studies, to our knowledge no comprehensive empirical search has been conducted. We demonstrate a powerful and versatile method for global identification of previously undescribed ncRNAs by modulating an essential RNA processing pathway through the depletion of a key ribonucleoprotein enzyme component, and monitoring differential transcriptional activities with genome tiling arrays during the time course of the ribonucleoprotein depletion. The entire Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome was scanned during cell growth decay regulated by promoter-mediated depletion of Rpp1, an essential and functionally conserved protein component of the RNase P enzyme. In addition to most verified genes and ncRNAs, expression was detected in 98 antisense and intergenic regions, 74 that were further confirmed to contain previously undescribed RNAs. A class of ncRNAs, located antisense to coding regions of verified protein-coding genes, is discussed in this article. One member, HRA1, is likely involved in 18S rRNA maturation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

References
-
- Peng W. T., Robinson M. D., Mnaimneh S., Krogan N. J., Cagney G., Morris Q., Davierwala A. P., Grigull J., Yang X., Zhang W., et al. Cell. 2004;113:919–933. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D. P. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Stolc V., Gauhar Z., Mason C., Halasz G., van Batenburg M. F., Rifkin S. A., Hua S., Herreman T., Tongprasit W., Barbano P. E., et al. Science. 2004;306:655–660. - PubMed
-
- Bertone P., Stolc V., Royce T. E., Rozowsky J. S., Urban A. E., Zhu X., Rinn J. L., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., et al. Science. 2004;306:2242–2246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

