Mechanical stress-strain sensors embedded in cardiac cytoskeleton: Z disk, titin, and associated structures
- PMID: 16537787
- PMCID: PMC3241960
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00816.2005
Mechanical stress-strain sensors embedded in cardiac cytoskeleton: Z disk, titin, and associated structures
Abstract
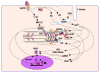
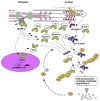
Cardiac muscle is equipped with intricate intrinsic mechanisms to regulate adaptive remodeling. Recent and extensive experimental findings powered by novel strategies for screening protein-protein interactions, improved imaging technologies, and versatile transgenic mouse methodologies reveal that Z disks and titin filaments possess unexpectedly complicated sensory and modulatory mechanisms for signal reception and transduction. These mechanisms employ molecules such as muscle-enriched LIM domain proteins, PDZ-LIM domain proteins, myozenin gene family members, titin-associated ankyrin repeat family proteins, and muscle-specific ring finger proteins, which have been identified as potential molecular sensor components. Moreover, classic transmembrane signaling processes, including mitogen-activated kinase, protein kinase C, and calcium signaling, also involve novel interactions with the Z disk/titin network. This compartmentalization of signaling complexes permits alteration of receptor-dependent transcriptional regulation by direct sensing of intrinsic stress. Newly identified mechanical stress sensors are not limited to Z-disk region and to I-band and M-band regions of titin but are also embedded in muscle-specific membrane systems such as the costamere, intercalated disks, and caveolae-like microdomains. This review summarizes current knowledge of this rapidly developing area with focus on how the heart adjusts physiological remodeling process to meet with mechanical demands and how this process fails in cardiac pathologies.
Figures



References
-
- Aikawa R, Komuro I, Yamazaki T, Zou Y, Kudoh S, Zhu W, Kadowaki T, Yazaki Y. Rho family small G proteins play critical roles in mechanical stress-induced hypertrophic responses in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 1999;84:458–466. - PubMed
-
- Allamand V, Campbell KP. Animal models for muscular dystrophy: valuable tools for the development of therapies. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:2459–2467. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Caroni P. Specificity of single LIM motifs in targeting and LIM/LIM interactions in situ. Genes Dev. 1996;10:289–300. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Halder G, Caroni P. Muscle LIM protein, a novel essential regulator of myogenesis, promotes myogenic differentiation. Cell. 1994;79:221–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

