Hydrops fetalis, cardiovascular defects, and embryonic lethality in mice lacking the calcitonin receptor-like receptor gene
- PMID: 16537897
- PMCID: PMC1430335
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.7.2511-2518.2006
Hydrops fetalis, cardiovascular defects, and embryonic lethality in mice lacking the calcitonin receptor-like receptor gene
Abstract
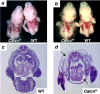
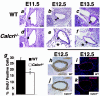
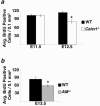
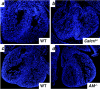
Adrenomedullin (AM) is a multifunctional peptide vasodilator that is essential for life. To date, numerous in vitro studies have suggested that AM can mediate its biological effects through at least three different receptors. To determine the in vivo importance of the most likely candidate receptor, calcitonin receptor-like receptor, a gene-targeted knockout model of the gene was generated. Mice heterozygous for the targeted Calcrl allele appear normal, survive to adulthood, and reproduce. However, heterozygote matings fail to produce viable Calcrl-/- pups, demonstrating that Calcrl is essential for survival. Timed matings confirmed that Calcrl-/- embryos die between embryonic day 13.5 (E13.5) and E14.5 of gestation. The Calcrl-/- embryos exhibit extreme hydrops fetalis and cardiovascular defects, including thin vascular smooth muscle walls and small, disorganized hearts remarkably similar to the previously characterized AM-/- phenotype. In vivo assays of cellular proliferation and apoptosis in the hearts and vasculature of Calcrl-/- and AM-/- embryos support the concept that AM signaling is a crucial mediator of cardiovascular development. The Calcrl gene targeted mice provide the first in vivo genetic evidence that CLR functions as an AM receptor during embryonic development.
Figures



References
-
- Aiyar, N., K. Rand, N. A. Elshourbagy, Z. Zeng, J. E. Adamou, D. J. Bergsma, and Y. Li. 1996. A cDNA encoding the calcitonin gene-related peptide type 1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 271:11325-11329. - PubMed
-
- Albertin, G., M. Rucinski, G. Carraro, M. Forneris, P. Andreis, L. K. Malendowicz, and G. G. Nussdorfer. 2005. Adrenomedullin and vascular endothelium growth factor genes are overexpressed in the regenerating rat adrenal cortex, and AM and VEGF reciprocally enhance their mRNA expression in cultured rat adrenocortical cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 16:431-435. - PubMed
-
- Allaker, R. P., and S. Kapas. 2003. Adrenomedullin and mucosal defence: interaction between host and microorganism. Regul. Pept. 112:147-152. - PubMed
-
- Autelitano, D. J. 1998. Cardiac expression of genes encoding putative adrenomedullin/calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 250:689-693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
