Excess of charged tRNALys maintains low levels of peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase in pth(Ts) mutants at a non-permissive temperature
- PMID: 16540595
- PMCID: PMC1408313
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl046
Excess of charged tRNALys maintains low levels of peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase in pth(Ts) mutants at a non-permissive temperature
Abstract
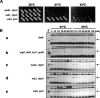
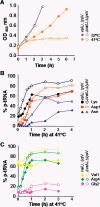
Cellular changes have been monitored during the suppression, mediated by the overproduction of tRNA(Lys), of thermosensitivity in Escherichia coli strain AA7852 carrying a mutation in peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase (Pth) encoded by the pth(Ts) gene. The presence in AA7852 cells of a plasmid bearing lysV gene helped to maintain low levels of the unstable Pth(Ts) protein and to preserve the viability of the mutant line at 41 degrees C whereas plasmids bearing other tRNA genes were ineffective. At 32 degrees C the excess of tRNA(Lys) did not alter the percentages of the free-, charged- or peptidyl-tRNA(Lys) species compared with those found in strains that did not overproduce tRNA(Lys). At 41 degrees C, however, despite increases in the level of peptidyl-tRNA(Lys), the excess tRNA(Lys) helped to maintain the concentration of charged-tRNA(Lys) at a level comparable with that found in non-overproducer cells grown at a permissive temperature. In addition, the excess tRNA(Lys) at 41 degrees C provoked a reduction in the concentrations of various peptidyl-tRNAs, which normally accumulate in pth(Ts) cells, and a proportional increase in the concentrations of the corresponding aminoacyl-tRNAs. The possible mechanism of rescue due to the overexpression of tRNA(Lys) and the causes of tRNA(Lys) starvation in pth(Ts) strains grown at non-permissive temperatures are considered.
Figures


References
-
- Atherly A.G., Menninger J.R. Mutant E.coli strain with temperature sensitive peptidyl-transfer RNA hydrolase. Nature New Biol. 1972;240:245–246. - PubMed
-
- Menninger J.R. The accumulation as peptidyl-transfer RNA of isoaccepting transfer RNA families in Escherichia coli with temperature-sensitive peptidyl-transfer RNA hydrolase. J. Biol. Chem. 1978;253:6808–6813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

