RNA-binding IMPs promote cell adhesion and invadopodia formation
- PMID: 16541107
- PMCID: PMC1440323
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601039
RNA-binding IMPs promote cell adhesion and invadopodia formation
Abstract
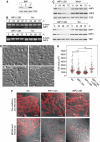
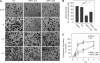
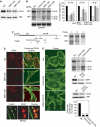
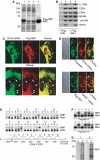
Oncofetal RNA-binding IMPs have been implicated in mRNA localization, nuclear export, turnover and translational control. To depict the cellular actions of IMPs, we performed a loss-of-function analysis, which showed that IMPs are necessary for proper cell adhesion, cytoplasmic spreading and invadopodia formation. Loss of IMPs was associated with a coordinate downregulation of mRNAs encoding extracellular matrix and adhesion proteins. The transcripts were present in IMP RNP granules, implying that IMPs were directly involved in the post-transcriptional control of the transcripts. In particular, we show that a 5.0 kb CD44 mRNA contained multiple IMP-binding sites in its 3'UTR, and following IMP depletion this species became unstable. Direct knockdown of the CD44 transcript mimicked the effect of IMPs on invadopodia, and we infer that CD44 mRNA stabilization may be involved in IMP-mediated invadopodia formation. Taken together, our results indicate that RNA-binding proteins exert profound effects on cellular adhesion and invasion during development and cancer formation.
Figures



References
-
- Atlas R, Behar L, Elliott E, Ginzburg I (2004) The insulin-like growth factor mRNA binding-protein IMP-1 and the Ras-regulatory protein G3BP associate with tau mRNA and HuD protein in differentiated P19 neuronal cells. J Neurochem 89: 613–626 - PubMed
-
- Bourguignon LY, Gunja-Smith Z, Iida N, Zhu HB, Young LJ, Muller WJ, Cardiff RD (1998) CD44v(3,8–10) is involved in cytoskeleton-mediated tumor cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) association in metastatic breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 176: 206–215 - PubMed
-
- Buccione R, Orth JD, McNiven MA (2004) Foot and mouth: podosomes, invadopodia and circular dorsal ruffles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 647–657 - PubMed
-
- Chuang YY, Tran NL, Rusk N, Nakada M, Berens ME, Symons M (2004) Role of synaptojanin 2 in glioma cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res 64: 8271–8275 - PubMed
-
- Condeelis J, Singer RH (2005) How and why does beta-actin mRNA target? Biol Cell 97: 97–110 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

