Novel orthotopic implantation model of human malignant pleural mesothelioma (EHMES-10 cells) highly expressing vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor
- PMID: 16542214
- PMCID: PMC11158536
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00163.x
Novel orthotopic implantation model of human malignant pleural mesothelioma (EHMES-10 cells) highly expressing vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor
Abstract
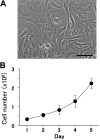
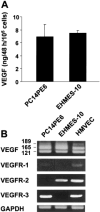
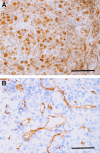
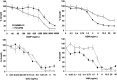
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is closely related to exposure to asbestos, and a rapid increase in the number of MPM patients in Japan is estimated in the years 2010-2050. The purpose of the present study was to establish a clinically relevant animal model that shows human patient-like progression of MPM. Here, we demonstrate that a human MPM cell line (EHMES-10) inoculated orthotopically (thoracic cavity) into severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice produces highly vascularized thoracic tumors with pleural dissemination and bloody pleural effusions by 5 weeks, suggesting a patient-like progression of this cell line after orthotopic inoculation. EHMES-10 cells overexpressed vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a molecule responsible for malignant effusions, and its receptor. Treatment with cisplatin, but not gemcitabine, significantly inhibited the production of pleural effusions, but it was not effective for thoracic tumors, consistent with chemotherapy refractory characteristics of MPM in patients. Our patient-like orthotopic model using EHMES-10 cells overexpressing VEGF and its receptor may be useful for examining the molecular pathogenesis of MPM and may contribute to the development of novel treatment strategies for MPM.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The therapeutic efficacy of anti vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, bevacizumab, and pemetrexed against orthotopically implanted human pleural mesothelioma cells in severe combined immunodeficient mice.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Oct 1;13(19):5918-25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0501. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17908988
-
Restored expression of the MYO18B gene suppresses orthotopic growth and the production of bloody pleural effusion by human malignant pleural mesothelioma cells in SCID mice.Oncol Res. 2006;16(5):235-43. doi: 10.3727/000000006783981062. Oncol Res. 2006. PMID: 17294804
-
E7080, a multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses the progression of malignant pleural mesothelioma with different proangiogenic cytokine production profiles.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Dec 1;15(23):7229-37. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1980. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19934291
-
Antiangiogenic therapies for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jan 1;16(2):740-8. doi: 10.2741/3716. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196199 Review.
-
[Systemic Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017 Dec;44(13):2041-2047. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017. PMID: 29361614 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Characterization of human malignant mesothelioma cell lines orthotopically implanted in the pleural cavity of immunodeficient mice for their ability to grow and form metastasis.BMC Cancer. 2006 May 17;6:130. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-130. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16704740 Free PMC article.
-
A p53-stabilizing agent, CP-31398, induces p21 expression with increased G2/M phase through the YY1 transcription factor in esophageal carcinoma defective of the p53 pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 1;9(1):79-93. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30755813 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity of alectinib in tumor cells with NCOA4-RET.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(43):73766-73773. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17900. eCollection 2017 Sep 26. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29088743 Free PMC article.
-
Possible Therapeutic Utility of anti-Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 Antibodies for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 12;10:945007. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.945007. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35903548 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of a third generation bisphosphonate and replication-competent adenoviruses augments the cytotoxicity on mesothelioma.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 12;16:455. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2483-y. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27405588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Light RW. Pleural Diseases, 4th edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, 2001.
-
- Broaddus VC. Asbestos, the mesothelial cell and malignancy: a matter of life or death. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1997; 17: 657–9. - PubMed
-
- Morinaga K, Kishimoto T, Sakatani M, Akira M, Yokoyama K, Sera Y. Asbestos‐related lung cancer and mesothelioma in Japan. Industrial Health 2001; 39: 65–74. - PubMed
-
- Mineral fiber content of lungs in patients with mesothelioma seeking compensation in Quebec. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996; 153: 711–18. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman RM. Patient‐like models of human cancer in mice. A review and critique of their development. Curr Perspect Mol Cell Oncol 1992; 1: 311–29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

