The Saccharomyces cerevisiae histone H2A variant Htz1 is acetylated by NuA4
- PMID: 16543219
- PMCID: PMC1413285
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1388106
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae histone H2A variant Htz1 is acetylated by NuA4
Abstract
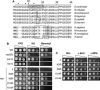
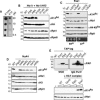
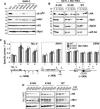
The histone H2A variant H2A.Z (Saccharomyces cerevisiae Htz1) plays roles in transcription, DNA repair, chromosome stability, and limiting telomeric silencing. The Swr1-Complex (SWR-C) inserts Htz1 into chromatin and shares several subunits with the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase. Furthermore, mutants of these two complexes share several phenotypes, suggesting they may work together. Here we show that NuA4 acetylates Htz1 Lys 14 (K14) after the histone is assembled into chromatin by the SWR-C. K14 mutants exhibit specific defects in chromosome transmission without affecting transcription, telomeric silencing, or DNA repair. Function-specific modifications may help explain how the same component of chromatin can function in diverse pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Carr A.M., Dorrington S.M., Hindley J., Phear G.A., Aves S.J., Nurse P. Analysis of a histone H2A variant from fission yeast: Evidence for a role in chromosome stability. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994;245:628–635. - PubMed
-
- Choy J.S., Tobe B.T., Huh J.H., Kron S.J. Yng2p-dependent NuA4 histone H4 acetylation activity is required for mitotic and meiotic progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:43653–43662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
