CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein mediates carbon monoxide-induced suppression of cyclooxygenase-2
- PMID: 16543610
- PMCID: PMC2643257
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0154OC
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein mediates carbon monoxide-induced suppression of cyclooxygenase-2
Abstract
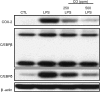
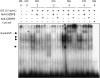
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is a key enzyme involved in the inflammatory process that is rapidly induced in macrophages in response to LPS. Carbon monoxide (CO), a byproduct of heme oxygnease-1, can suppress proinflammatory response in various in vitro and in vivo models of inflammation. This study was undertaken to examine whether CO can regulate (and if so, to delineate the mechanism by which CO regulates) LPS-induced COX-2 expression in macrophages. RAW 264.7 murine macrophages were stimulated with LPS (0-10 ng/ml) with or without CO (500 ppm). Northern and Western blot analysis was done. Progstaglandin E(2) and nitrite concentration was measured from cell culture supernatant. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay was performed to assess nuclear factor binding. CO downregulated LPS-induced COX-2 mRNA and protein expression. CO also inhibited LPS-induced prostaglandin E(2) secretion (P < 0.05). CO also decreased LPS-induced CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) beta and delta protein expression in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells. Gel shift analysis revealed that CO treatment decreased LPS-induced activation of protein binding to C/EBP consensus oligonucleotides of murine cyclooxygenase-2 promoter. CO also decreased LPS-induced nitric oxide synthase-2 protein expression and nitrite production, and decreased LPS-induced activation of protein binding to C/EBP consensus oligonucleotides of murine nitric oxide synthase-2 promoter. CO may act as an important regulator of inflammation by virtue of its ability to regulate C/EBPs.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase, TNF-alpha and COX-2 expression by sauchinone effects on I-kappaBalpha phosphorylation, C/EBP and AP-1 activation.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 May;139(1):11-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705231. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12746218 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of LPS-induced C/EBP delta by trichostatin A has a positive effect on LPS-induced cyclooxygenase 2 expression in RAW264.7 cells.J Cell Biochem. 2010 Aug 15;110(6):1430-8. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22682. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20506344
-
Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by heat shock protein 60 in macrophages and endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002 Oct;283(4):C1267-77. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00609.2001. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12225989
-
Ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone from Inula britannica, inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inactivation of NF-kappaB.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jun;133(4):503-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704099. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11399667 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon monoxide induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression through MAPKs and PKG in phagocytes.Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Dec;10(12):1520-5. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.08.026. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20840837
Cited by
-
Anti‑inflammatory effects of methanol extract from Peperomia dindygulensis Miq. mediated by HO‑1 in LPS‑induced RAW 264.7 cells.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Jun 14;28(2):317. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12606. eCollection 2024 Aug. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38939180 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ribes diacanthum Pall Mediated via Regulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages and a TPA-Induced Dermatitis Animal Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jul 15;9(7):622. doi: 10.3390/antiox9070622. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32679895 Free PMC article.
-
In silico analysis and experimental validation of molecular mechanisms of salvianolic acid A-inhibited LPS-stimulated inflammation, in RAW264.7 macrophages.Cell Prolif. 2013 Oct;46(5):595-605. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12056. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Cell Prolif. 2013. PMID: 24033467 Free PMC article.
-
Role of heme oxygenase-1 in postnatal differentiation of stem cells: a possible cross-talk with microRNAs.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Apr 10;20(11):1827-50. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5341. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24053682 Free PMC article.
-
The Stem Bark of Kalopanax pictus Exhibits Anti-inflammatory Effect through Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction and NF-κB Suppression.Immune Netw. 2010 Dec;10(6):212-8. doi: 10.4110/in.2010.10.6.212. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Immune Netw. 2010. PMID: 21286382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morse D, Choi AM. Heme oxygenase-1: the “emerging molecule” has arrived. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002;27:8–16. - PubMed
-
- Otterbein L, Sylvester SL, Choi AM. Hemoglobin provides protection against lethal endotoxemia in rats: the role of heme oxygenase-1. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1995;13:595–601. - PubMed
-
- Morse D, Pischke SE, Zhou Z, Davis RJ, Flavell RA, Loop T, Otterbein SL, Otterbein LE, Choi AM. Suppression of inflammatory cytokine production by carbon monoxide involves the JNK pathway and AP-1. J Biol Chem 2003;278:36993–36998. - PubMed
-
- Otterbein LE, Bach FH, Alam J, Soares M, Tao Lu H, Wysk M, Davis RJ, Flavell RA, Choi AM. Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Nat Med 2000;6:422–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

