The neutrophil-activating protein of Helicobacter pylori promotes Th1 immune responses
- PMID: 16543949
- PMCID: PMC1401483
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI27177
The neutrophil-activating protein of Helicobacter pylori promotes Th1 immune responses
Abstract
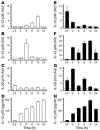
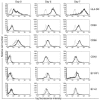
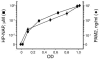
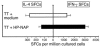
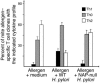
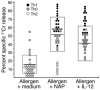
The Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein (HP-NAP) is a virulence factor of H. pylori that stimulates in neutrophils high production of oxygen radicals and adhesion to endothelial cells. We report here that HP-NAP is a TLR2 agonist able to induce the expression of IL-12 and IL-23 by neutrophils and monocytes. Addition in culture of HP-NAP, as an immune modulator, to antigen-induced T cell lines resulted in a remarkable increase in the number of IFN-gamma-producing T cells and decrease of IL-4-secreting cells, thus shifting the cytokine profile of antigen-activated human T cells from Th2 to a Th1 cytotoxic phenotype. We also found that in vivo HP-NAP elicited an antigen-specific Th1-polarized T cell response in the gastric mucosa of H. pylori-infected patients. These data indicate HP-NAP as an important factor of H. pylori able to elicit cells of the innate immune system to produce IL-12 and IL-23, and they suggest it as a new tool for promoting Th1 immune responses.
Figures
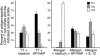
References
-
- Marshall B.J., Warren J.R. Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1984;1:1311–1315. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin C.S. Helicobacter pylori gastritis, peptic ulcer and gastric cancer: clinical and molecular aspects. . Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997;25:1017–1019. - PubMed
-
- Parsonnet J., et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric lymphoma. . N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;330:1267–1271. - PubMed
-
- Dixon M.F., Genta R.M., Yardley J.H., Correa P. Classification and grading of gastritis. . Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996;20:1161–1181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

