Liberation of zinc-containing L31 (RpmE) from ribosomes by its paralogous gene product, YtiA, in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 16547061
- PMCID: PMC1428384
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.188.7.2715-2720.2006
Liberation of zinc-containing L31 (RpmE) from ribosomes by its paralogous gene product, YtiA, in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
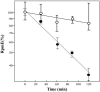
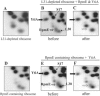
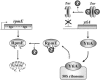
We have found that alternative localization of two types of L31 ribosomal protein, RpmE and YtiA, is controlled by the intracellular concentration of zinc in Bacillus subtilis. The detailed mechanisms for the alternation of L31 proteins under zinc-deficient conditions were previously unknown. To obtain further information about this regulatory mechanism, we have studied the stability of RpmE in vivo and the binding affinity of these proteins to ribosomes in vitro, and we have found that liberation of RpmE from ribosomes is triggered by the expression of ytiA, which is induced by the derepression of Zur under zinc-deficient conditions.
Figures


References
-
- Eistetter, A. J., P. D. Butler, R. R. Traut, and T. G. Fanning. 1999. Characterization of Escherichia coli 50S ribosomal protein L31. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 180:345-349. - PubMed
-
- Hardy, S. J. S., C. G. Kurland, P. Voynow, and G. Mora. 1969. The ribosomal proteins of Eschericha coli. I. Purification of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry 8:2897-2905. - PubMed
-
- Henne, A., H. Bruggemann, C. Raasch, A. Wiezer, T. Hartsch, H. Liesegang, A. Johann, T. Lienard, O. Gohl, R. Martinez-Arias, C. Jacobi, V. Starkuviene, S. Schlenczeck, S. Dencker, R. Huber, H. P. Klenk, W. Kramer, R. Merk, G. Gottschalk, and H. J. Fritz. 2004. The genome sequence of the extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus. Nat. Biotechnol. 22:547-553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

