Complications associated with the bacille Calmette-Guérin vaccination in Ireland
- PMID: 16547086
- PMCID: PMC2082825
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2005.078972
Complications associated with the bacille Calmette-Guérin vaccination in Ireland
Abstract
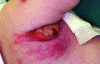
Introduction: BCG vaccination is currently recommended for all newborns in Ireland except where specifically contraindicated. This paper describes a marked increase in the number of referrals of patients with localised complications after vaccination to two Dublin paediatric hospitals. This increase coincided with the introduction of a new strain of BCG vaccine
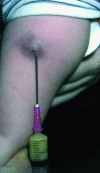
Methods: A population surveillance study was undertaken to determine the frequency and spectrum of complications associated with the new strain of BCG vaccine introduced in Ireland. Patients were identified though review of the infectious disease service case records and microbiology laboratory culture reports for the two year period from August 2002 to July 2004. Prospectively gathered data were supplemented by retrospective chart review. All infants who had inoculation site abscesses, suppurative adenopathy, or non-suppurative adenopathy with nodes > or =2 cm were included.
Results: Fifty eight patients presented a median of 13 weeks post-inoculation: 32 with suppurative adenitis, 17 with inoculation site abscess, three with both inoculation site abscess and suppurative adenitis, and six with non-suppurative adenopathy. The overall complication rate was estimated at 1/931 vaccinees with 1/1543 developing suppurative adenitis. Twenty six infants required surgery.
Discussion: This series illustrates the role of hospitals in sentinel surveillance and highlights the importance of having a well functioning and responsive system of adverse event reporting. These events raise a serious question as to the suitability of this vaccine strain for use in a national immunisation programme in a country where the prevalence of tuberculous disease is 10.4/100,000.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none declared
References
-
- Dunleavy M. The prevention of tuberculosis. Ir J Med Sci 19521–10. - PubMed
-
- Royal College of Physicians in Ireland National Immunisation Advisory Committee Guidelines. July 2002
-
- Shannon A, Kelly P. Isoniazid resistant tuberculosis in a school outbreak: the protective effect of BCG. Eur Respir J 19914778–792. - PubMed
-
- Stinson J, Kelly P. National Tuberculosis Survey (1986). Ir Med J 1988817–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical