The adaptor protein soc-1/Gab1 modifies growth factor receptor output in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 16547100
- PMCID: PMC1461424
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.055822
The adaptor protein soc-1/Gab1 modifies growth factor receptor output in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
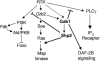
Previous genetic analysis has shown that dos/soc-1/Gab1 functions positively in receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-stimulated Ras/Map kinase signaling through the recruitment of csw/ptp-2/Shp2. Using sensitized assays in Caenorhabditis elegans for let-23/Egfr and daf-2/InsR (insulin receptor-like) signaling, it is shown that soc-1/Gab1 inhibits phospholipase C-gamma (PLCgamma) and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase (PI3K)-mediated signaling. Furthermore, as well as stimulating Ras/Map kinase signaling, soc-1/Gab1 stimulates a poorly defined signaling pathway that represses class 2 daf-2 phenotypes. In addition, it is shown that SOC-1 binds the C-terminal SH3 domain of SEM-5. This binding is likely to be functional as the sem-5(n2195)G201R mutation, which disrupts SOC-1 binding, behaves in a qualitatively similar manner to a soc-1 null allele in all assays for let-23/Egfr and daf-2/InsR signaling that were examined. Further genetic analysis suggests that ptp-2/Shp2 mediates the negative function of soc-1/Gab1 in PI3K-mediated signaling, as well as the positive function in Ras/Map kinase signaling. Other effectors of soc-1/Gab1 are likely to inhibit PLCgamma-mediated signaling and stimulate the poorly defined signaling pathway that represses class 2 daf-2 phenotypes. Thus, the recruitment of soc-1/Gab1, and its effectors, into the RTK-signaling complex modifies the cellular response by enhancing Ras/Map kinase signaling while inhibiting PI3K and PLCgamma-mediated signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Battu, G., E. F. Hoier and A. Hajnal, 2003. The C. elegans G-protein-coupled receptor SRA-13 inhibits RAS/MAPK signalling during olfaction and vulval development. Development 130: 2567–2577. - PubMed
-
- Bausenwein, B. S., M. Schmidt, B. Mielke and T. Raabe, 2000. In vivo functional analysis of the daughter of sevenless protein in receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mech. Dev. 90: 205–215. - PubMed
-
- Beitel, G. J., S. G. Clark and H. R. Horvitz, 1990. Caenorhabditis elegans ras gene let-60 acts as a switch in the pathway of vulval induction. Nature 348: 503–509. - PubMed
-
- Clandinin, T. R., J. A. DeModena and P. W. Sternberg, 1998. Inositol trisphosphate mediates a RAS-independent response to LET-23 receptor tyrosine kinase activation in C. elegans. Cell 92: 523–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

