X-chromosome targeting and dosage compensation are mediated by distinct domains in MSL-3
- PMID: 16547465
- PMCID: PMC1479548
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400658
X-chromosome targeting and dosage compensation are mediated by distinct domains in MSL-3
Abstract
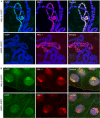
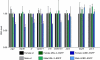
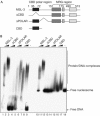
In Drosophila, dosage compensation of X-linked genes is achieved by transcriptional upregulation of the male X chromosome. Genetic and biochemical studies have demonstrated that male-specific lethal (MSL) proteins together with roX RNAs regulate this process. Here, we show that MSL-3 is essential for cell viability and that three domains in the protein have distinct roles in dosage compensation. The chromo-barrel domain (CBD) is not necessary for MSL targeting to the male X chromosome but is important for male viability and equalization of X-linked gene transcription. The polar region cooperates with the CBD in MSL-3 function, whereas the MRG domain is responsible for targeting the protein to the X chromosome. Our results demonstrate that MSL-3 localization to the male X chromosome and transcriptional upregulation of X-linked genes are two separable functions of the MSL-3 protein.
Figures


References
-
- Akhtar A, Becker PB (2000) Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol Cell 5: 367–375 - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A, Zink D, Becker PB (2000) Chromodomains are protein–RNA interaction modules. Nature 407: 405–409 - PubMed
-
- Bertram MJ, Pereira-Smith OM (2001) Conservation of the MORF4 related gene family: identification of a new chromo domain subfamily and novel protein motif. Gene 266: 111–121 - PubMed
-
- Buscaino A, Kocher T, Kind JH, Holz H, Taipale M, Wagner K, Wilm M, Akhtar A (2003) MOF-regulated acetylation of MSL-3 in the Drosophila dosage compensation complex. Mol Cell 11: 1265–1277 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

