Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of rhabdomyosarcoma cells reveal differential cellular gene expression in response to enterovirus 71 infection
- PMID: 16548883
- PMCID: PMC7162300
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00644.x
Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of rhabdomyosarcoma cells reveal differential cellular gene expression in response to enterovirus 71 infection
Abstract
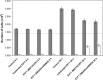
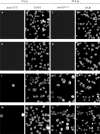
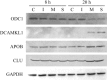
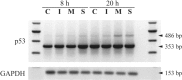
Insights into the host antiviral strategies as well as viral disease manifestations can be achieved through the elucidation of host- and virus-mediated transcriptional responses. An oligo-based microarray was employed to analyse mRNAs from rhabdomyosarcoma cells infected with the MS/7423/87 strain of enterovirus 71 (EV71) at 20 h post infection. Using Acuity software and LOWESS normalization, 152 genes were found to be downregulated while 39 were upregulated by greater than twofold. Altered transcripts include those encoding components of cytoskeleton, protein translation and modification; cellular transport proteins; protein degradation mediators; cell death mediators; mitochondrial-related and metabolism proteins; cellular receptors and signal transducers. Changes in expression profiles of 15 representative genes were authenticated by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), which also compared the transcriptional responses of cells infected with EV71 strain 5865/Sin/000009 isolated from a fatal case during the Singapore outbreak in 2000. Western blot analyses of APOB, CLU, DCAMKL1 and ODC1 proteins correlated protein and transcript levels. Two-dimensional proteomic maps highlighted differences in expression of cellular proteins (CCT5, CFL1, ENO1, HSPB1, PSMA2 and STMN1) following EV71 infection. Expression of several apoptosis-associated genes was modified, coinciding with apoptosis attenuation observed in poliovirus infection. Interestingly, doublecortin and CaM kinase-like 1 (DCAMKL1) involved in brain development, was highly expressed during infection. Thus, microarray, real-time RT-PCR and proteomic analyses can elucidate the global view of the numerous and complex cellular responses that contribute towards EV71 pathogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Agirre, A. , Barco, A. , Carrasco, L. , Nieva, J.L. (2002) Viroporin‐mediated membrane permeabilization. Pore formation by nonstructural poliovirus 2B protein. J Biol Chem 277: 40434–40441. - PubMed
-
- Almog, N. , Goldfinger, N. , Rotter, V. (2000) p53‐dependent apoptosis is regulated by a C‐terminally alternatively spliced form of murine p53. Oncogene 19: 3395–3403. - PubMed
-
- Ayyavoo, V. , Mahboubi, A. , Mahalingam, S. , Ramalingam, R. , Kudchodkar, S. , Williams, W.V. , et al. (1997) HIV‐1 Vpr suppresses immune activation and apoptosis through regulation of nuclear factor kappa B. Nat Med 3: 1117–1123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

