Regulation of the insulin gene by glucose and fatty acids
- PMID: 16549443
- PMCID: PMC1853259
- DOI: 10.1093/jn/136.4.873
Regulation of the insulin gene by glucose and fatty acids
Abstract
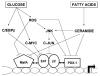
The insulin gene is expressed almost exclusively in pancreatic beta-cells. Metabolic regulation of insulin gene expression enables the beta-cell to maintain adequate stores of intracellular insulin to sustain the secretory demand. Glucose is the major physiologic regulator of insulin gene expression; it coordinately controls the recruitment of transcription factors [e.g., pancreatic/duodenal homeobox-1 (PDX-1), mammalian homologue of avian MafA/L-Maf (MafA), Beta2/Neuro D (B2), the rate of transcription, and the stability of insulin mRNA. However, chronically elevated levels of glucose (glucotoxicity) and lipids (lipotoxicity) also contribute to the worsening of beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes, in part via inhibition of insulin gene expression. The mechanisms of glucotoxicity, which involve decreased binding activities of PDX-1 and MafA and increased activity of C/EBPbeta, are mediated by high-glucose-induced generation of oxidative stress. On the other hand, lipotoxicity is mediated by de novo ceramide synthesis and involves inhibition of PDX-1 nuclear translocation and MafA gene expression. Glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity have common targets, which makes their combination particularly harmful to insulin gene expression and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Poitout V, Stein R, Rhodes CJ. Insulin gene expression and biosynthesis. In: DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Keen H, Zimmet P, editors. International textbook of diabetes mellitus. 3. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons; 2004. pp. 98–123.
-
- Jonsson J, Carlsson L, Edlund T, Edlund H. Insulin-promoter factor 1 is required for pancreatic development in mice. Nature. 1994;371:606–9. - PubMed
-
- Peers B, Leonard J, Sharma S, Teitelman G, Montminy MR. Insulin expression in pancreatic islet cells relies on cooperative interactions between the helix loop helix factor E47 and the homeobox factor STF-1. Mol Endocrinol. 1994;8:1798–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

