TEX14 is essential for intercellular bridges and fertility in male mice
- PMID: 16549803
- PMCID: PMC1458781
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505123103
TEX14 is essential for intercellular bridges and fertility in male mice
Abstract
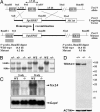
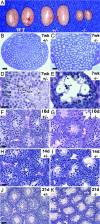
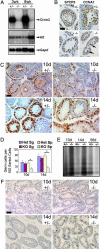
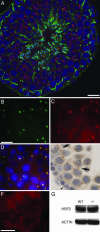
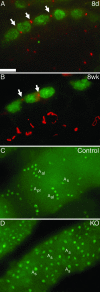
Cytokinesis in somatic cells concludes with the formation of a midbody, which is abscised to form individual daughter cells. In contrast, germ cell cytokinesis results in a permanent intercellular bridge connecting the daughter cells through a large cytoplasmic channel. During spermatogenesis, proposed roles for the intercellular bridge include germ cell communication, synchronization, and chromosome dosage compensation in haploid cells. Although several essential components of the midbody have recently been identified, essential components of the vertebrate germ cell intercellular bridge have until now not been described. Herein, we show that testis-expressed gene 14 (TEX14) is a novel protein that localizes to germ cell intercellular bridges. In the absence of TEX14, intercellular bridges are not observed by using electron microscopy and other markers. Spermatogenesis in Tex14(-/-) mice progresses through the transit amplification of diploid spermatogonia and the expression of early meiotic markers but halts before the completion of the first meiotic division. Thus, TEX14 is required for intercellular bridges in vertebrate germ cells, and these studies provide evidence that the intercellular bridge is essential for spermatogenesis and fertility.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F30MH066542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD47514/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD012629/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD044858/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM07330/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD12629/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD07495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH066542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD42454/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD042454/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007330/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD012629/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HD047514/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD44858/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

