IL-4 induced MUC4 enhancement in respiratory epithelial cells in vitro is mediated through JAK-3 selective signaling
- PMID: 16551361
- PMCID: PMC1435893
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-39
IL-4 induced MUC4 enhancement in respiratory epithelial cells in vitro is mediated through JAK-3 selective signaling
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have identified MUC4 mucin as a ligand for activation of ErbB2, a receptor tyrosine kinase that modulates epithelial cell proliferation following epithelial damage in airways of asthmatics. In this study, we investigated the potential role of IL-4, one of the Th2 inflammatory cytokines persistent in asthmatic airways, in regulating MUC4 expression using a cell line NCI-H650.
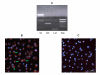
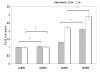
Methods: Real time PCR analysis was performed to determine concentration and time dependent effects of IL-4 upon MUC4 expression. Nuclear run on experiments were carried out to explore potential transcriptional modulation. Western blotting experiments using a monoclonal antibody specific to ASGP-2 domain of MUC4 were performed to analyze MUC4 glycoprotein levels in plasma membrane fractions. To analyze potential signal transduction cascades, IL-4 treated confluent cultures were co-incubated, separately with a pan-JAK inhibitor, a JAK-3 selective inhibitor or a MEK-1, 2 (MAPK) inhibitor at various concentrations before MUC4 transcript analysis. Corresponding transcription factor activation was tested by western blotting using a monoclonal p-STAT-6 antibody.
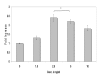
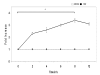
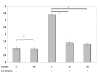
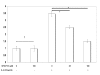
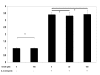
Results: MUC4 levels increased in a concentration and time specific fashion reaching peak expression at 2.5 ng/ml and 8 h. Nuclear run on experiments revealed transcriptional enhancement. Corresponding increases in MUC4 glycoprotein levels were observed in plasma membrane fractions. Pan-JAK inhibitor revealed marked reduction in IL-4 stimulated MUC4 levels and JAK3 selective inhibitor down-regulated MUC4 mRNA expression in a concentration-dependent fashion. In accordance with the above observations, STAT-6 activation was detected within 5 minutes of IL-4 stimulus. No effect in MUC4 levels was observed on using a MAPK inhibitor.
Conclusion: These observations signify a potential role for IL-4 in MUC4 up-regulation in airway epithelia.
Figures
References
-
- Fahy JV. Remodeling of the airway epithelium in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:S46–51. - PubMed
-
- Laitinen LA, Heino M, Laitinen A, Kava T, Haahtela T. Damage of the airway epithelium and bronchial reactivity in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;131:599–606. - PubMed
-
- Frew AJ, Moqbel R, Azzawi M, Hartnell A, Barkans J, Jeffery PK, Kay AB, Scheper RJ, Varley J, Church MK, et al. T lymphocytes and eosinophils in allergen-induced late-phase asthmatic reactions in the guinea pig. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;141:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Azzawi M, Bradley B, Jeffery PK, Frew AJ, Wardlaw AJ, Knowles G, Assoufi B, Collins JV, Durham S, Kay AB. Identification of activated T lymphocytes and eosinophils in bronchial biopsies in stable atopic asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;142:1407–1413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

