Reversible cytotoxic cerebral edema in cerebral fat embolism
- PMID: 16552005
- PMCID: PMC7976969
Reversible cytotoxic cerebral edema in cerebral fat embolism
Abstract
We present a case of cerebral fat embolism (CFE) that demonstrated evidence of diffuse white matter cytotoxic edema on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging, in addition to punctate hyperintensities on T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted imaging. The case suggests that CFE represents a combination of occlusive arteriolar disease and secondary neurotoxicity.
Figures
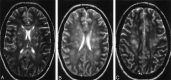
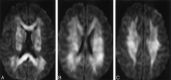
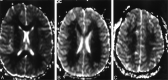
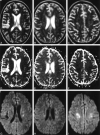
References
-
- Finlay ME, Benson MD. Case report: magnetic resonance imaging in cerebral fat embolism. Clin Radiol 1996;51:445–46 - PubMed
-
- Marshall GB, Heele VR, Heux L, et al. Magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging in cerebral fat embolism. Can J Neurol Sci 2004;31:417–21 - PubMed
-
- Parizel PM, Demey HE, Veeckmans G, et al. Early diagnosis of cerebral fat embolism syndrome by diffusion-weighted MRI (starfield pattern). Stroke 2001;32:2942–44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
