Basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland: MR imaging findings with pathologic correlation
- PMID: 16552019
- PMCID: PMC7976949
Basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland: MR imaging findings with pathologic correlation
Abstract
Background and purpose: Basal cell adenomas (BCAs) are rare tumors of the parotid gland. Only a few case reports describing MR imaging features of BCA have been published. The aim of this study was to describe and characterize the MR findings of BCAs of the parotid gland.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively reviewed MR images of BCA with pathologic correlation in 8 cases (2 men and 6 women; age range, 52-82 years) collected between January 1992 and August 2004 from our pathologic data base. All MR images were retrospectively evaluated with respect to the marginal morphology, signal intensity (SI), and enhancement behavior by 2 experienced radiologists.
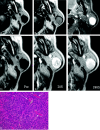
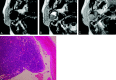
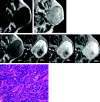
Results: On pathologic examination, 5 tumors were solid type, 2 were trabecular type, and 1 was membranous type. All of the tumors were well circumscribed with smooth contours. Cystic changes were seen in 4 cases. On T1-weighted images (T1WI), 7 tumors showed homogeneously low SI equal to muscle and one showed heterogeneously low SI. On T2-weighted images (T2WI), all of them showed slightly lower SI than that of surrounding parotid tissue. On gadolinium-enhanced T1WI, 6 tumors demonstrated moderate enhancement and one demonstrated strong enhancement (membranous type). Dynamic studies were performed in 4 cases. All showed rapid and prolonged enhancement.
Conclusion: MR imaging findings of BCA were well-defined and smooth marginal morphologies, relatively low SI on both T11W and T2WI, and rapid and prolonged enhancement on dynamic study. Although BCAs are rare, they should be suspected when a tumor shows all of the characteristics noted here.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland: MR imaging findings].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2011 Dec;20(6):648-52. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2011. PMID: 22241320 Chinese.
-
Basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland; MR features and differentiation from pleomorphic adenoma.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2016;45(4):20150322. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20150322. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26837669 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of MR imaging findings differentiating parotid basal cell adenomas from other parotid tumors.Eur J Radiol. 2021 Nov;144:109980. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109980. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Eur J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34601323
-
Basal cell adenoma with extensive squamous metaplasia and cellular atypia: a case report with cytohistopathological correlation and review of the literature.Diagn Cytopathol. 2012 Jan;40(1):48-55. doi: 10.1002/dc.21584. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012. PMID: 22180238 Review.
-
A retrospective study of 30 basal cell adenomas of the salivary gland in a Brazilian population and literature review.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Jul;278(7):2447-2454. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06331-x. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 32886182 Review.
Cited by
-
Salivary gland tumors of the parotid gland: CT and MR imaging findings with emphasis on intratumoral cystic components.Neuroradiology. 2014 Sep;56(9):789-95. doi: 10.1007/s00234-014-1386-3. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Neuroradiology. 2014. PMID: 24948426
-
Basal cell adenoma in the parapharyngeal space resected via trans-oral approach aided by endoscopy: Case series and a review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(34):e11837. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011837. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30142775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basal cell adenoma and myoepithelioma of the parotid gland: patterns of enhancement at two-phase CT in comparison with Warthin tumor.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019 Jul;25(4):285-290. doi: 10.5152/dir.2019.18337. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31120425 Free PMC article.
-
Cystic lesions of the parotid gland: radiologic-pathologic correlation according to the latest World Health Organization 2017 Classification of Head and Neck Tumours.Jpn J Radiol. 2017 Nov;35(11):629-647. doi: 10.1007/s11604-017-0678-z. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Jpn J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28836142 Review.
-
Comparative Study of Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and the Diagnostic Value of B-Mode and Color Doppler for Common Benign Tumors in the Parotid Gland.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 7;11:669542. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.669542. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34307139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seifert G, Sobin LH. Histological typing of salivary gland tumors. In: World Health Organization international histological classification of tumors. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;1991. :20–21
-
- Ellis GL, Auclair PL. Tumors of the salivary gland. In: Atlas of tumor pathology. 3rd series, fascicle 17. Washington DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology;1996. :80–94
-
- Gnepp DR, Brandwein MS, Henley JD. Salivary and lacrimal glands. In: Gnepp DR, ed. Diagnostic surgical pathology of the head and neck. 1st ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2000. :325–430
-
- Nagao K, Matsuzaki O, Saiga H, et al. Histopathologic studies of basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland. Cancer 1982;50:736–45 - PubMed
-
- Som PM, Brandwein MS. Salivary glands: anatomy and pathology. In: Som PM, Curtin HD, eds. Head and neck imaging. St. Louis: Mosby;2003. :2084–86
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
