Correction of extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis by the mesenteric to left portal vein bypass
- PMID: 16552203
- PMCID: PMC1448975
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000205827.73706.97
Correction of extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis by the mesenteric to left portal vein bypass
Abstract
Objective: The goal of this study was to determine the effectiveness of mesenteric vein to left portal vein bypass operation (MLPVB) in correcting extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis (EHPVT) in children. The treatment of idiopathic EHPVT has been primarily palliative, whereas MLPVB restores hepatic portal flow in patients with EHPVT.
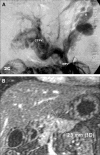
Methods: Thirty-four children with symptomatic EHPVT underwent surgery with intent to perform MLPVB and were followed for up to 7 years. MLPVB was successful in 31 patients (91%), all of whom maintain patent vein grafts and have symptomatic relief of EHPVT in follow-up. All patients had complete relief from gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with hypersplenism had significant increases in platelet and leukocyte counts and reduction in spleen size. Superior mesenteric vein flow increased from 119 +/- 66 mL/min before bypass to 447 +/- 225 mL/min (P < 0.0001) after surgery. Postoperative blood flow in the bypass graft expressed as a fraction of calculated ideal portal flow for size correlated inversely with age (P < 0.001). Left-portal vein diameter increased from 2.6 +/- 1.6 mm to 7.3 +/- 2.4 mm 2 years after surgery (P < 0.002). Liver volume increased from 703 +/- 349 cm3 to 799 +/- 351 cm3 1 week after surgery (P < 0.001). Prothrombin time improved to normal in all patients 1 year after surgery.
Conclusions: MLPVB provides excellent relief of symptoms in children with idiopathic EHPVT and results in liver growth and normalization of coagulation parameters. This surgery is corrective and should be done at as early an age as possible.
Figures



References
-
- Alonso EM, Hackworth C, Whitington PF. Portal hypertension in children. Clin Liver Dis. 1997;1:201–222. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez F, Bernard O, Brunelle F, et al. Portal obstruction in children: I. Clinical investigation and hemorrhage risk. J Pediatr. 1983;103:696–702. - PubMed
-
- Fonkalsrud EW. Long-term results following surgical management of portal hypertension in children. Z Kinderchir. 1982;35:57–61. - PubMed
-
- Orloff MJ, Orloff MS, Girard B, et al. Bleeding esophagogastric varices from extrahepatic portal hypertension: 40 years’ experience with portal-systemic shunt. J Am Coll Surg. 2002;194:717–728. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

