Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in the carcinogenesis of gastrointestinal tract cancers: a review and report of personal experience
- PMID: 16552798
- PMCID: PMC4124307
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i9.1336
Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in the carcinogenesis of gastrointestinal tract cancers: a review and report of personal experience
Abstract
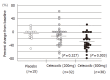
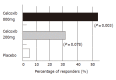
Selective cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitors (coxibs) were developed as one of the anti-inflammatory drugs to avoid the various side effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). However,coxibs also have an ability to inhibit tumor development of various kinds the same way that NSAIDs do. Many experimental studies using cell lines and animal models demonstrated an ability to prevent tumor proliferation of COX-2 inhibitors. After performing a randomized study for polyp chemoprevention study in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP),which showed that the treatment with celecoxib, one of the coxibs, significantly reduced the number of colorectal polyps in 2000, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) immediately approved the clinical use of celecoxib for FAP patients. However, some coxibs were recently reported to increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events including heart attack and stroke. In this article we review a role of COX-2 in carcinogenesis of gastrointestinal tract, such as the esophagus, stomach and colorectum,and also analyze the prospect of coxibs for chemoprevention of gastrointestinal tract tumors.
Figures


References
-
- Farrow DC, Vaughan TL, Hansten PD, Stanford JL, Risch HA, Gammon MD, Chow WH, Dubrow R, Ahsan H, Mayne ST, et al. Use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1998;7:97–102. - PubMed
-
- Thun MJ, Namboodiri MM, Calle EE, Flanders WD, Heath CW. Aspirin use and risk of fatal cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53:1322–1327. - PubMed
-
- Vane JR. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971;231:232–235. - PubMed
-
- Pai R, Soreghan B, Szabo IL, Pavelka M, Baatar D, Tarnawski AS. Prostaglandin E2 transactivates EGF receptor: a novel mechanism for promoting colon cancer growth and gastrointestinal hypertrophy. Nat Med. 2002;8:289–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

