Budesonide induces complete remission in autoimmune hepatitis
- PMID: 16552802
- PMCID: PMC4124311
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i9.1362
Budesonide induces complete remission in autoimmune hepatitis
Abstract
Aim: Prednisone and azathioprine represent the standard treatment for autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). However, only 65% of the patients enter complete histological remission. Recently, budesonide (BUD) was reported to be a promising alternative. In this study we assessed the efficacy and safety of BUD in AIH.
Methods: Eighteen patients (12 women, 6 men; mean age 45.4+/-21 years)with AIH were treated with BUD (Budenofalk) 3 mg thrice daily and followed up for at least 24 wk. Seven patients also had features of primary biliary cirrhosis (n=5) or primary sclerosing cholangitis (n=2). Advanced liver fibrosis or cirrhosis was present in 6 patients.
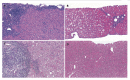
Results: Fifteen (83%) patients had a complete clinical and biochemical remission. Ten patients, including five with acute hepatitis,were given BUD as first-line therapy, of which seven enter remission. Three patients, two with liver cirrhosis, did not improve.All patients with second-line therapy experienced long-term remission. A histological remission was also seen in three patients. Clinically relevant BUD-induced side effects were recorded only in patients with liver cirrhosis (n=4).
Conclusion: BUD is effective in remission induction in the majority of our patients with AIH. Side effects and treatment failure was mainly observed in patients with liver cirrhosis.
Figures
References
-
- Manns MP, Strassburg CP. Autoimmune hepatitis: clinical challenges. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:1502–1517. - PubMed
-
- Czaja AJ, Bianchi FB, Carpenter HA, Krawitt EL, Lohse AW, Manns MP, McFarlane IG, Mieli-Vergani G, Toda G, Vergani D, et al. Treatment challenges and investigational opportunities in autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2005;41:207–215. - PubMed
-
- Clissold SP, Heel RC. Budesonide. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic efficacy in asthma and rhinitis. Drugs. 1984;28:485–518. - PubMed
-
- Thalen A, Brattsand R, Andersson PH. Development of glucocorticosteroids with enhanced ratio between topical and systemic effects. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1989;151:11–9; discussion 47-52. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, Bianchi L, Burroughs AK, Cancado EL, Chapman RW, Cooksley WG, Czaja AJ, Desmet VJ, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1999;31:929–938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

