Activation of kainate receptors sensitizes oligodendrocytes to complement attack
- PMID: 16554473
- PMCID: PMC6674098
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3780-05.2006
Activation of kainate receptors sensitizes oligodendrocytes to complement attack
Abstract
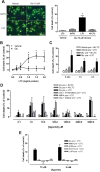
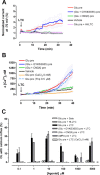
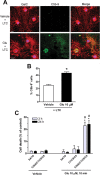
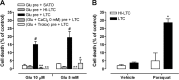
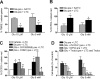
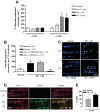
Glutamate excitotoxicity and complement attack have both been implicated separately in the generation of tissue damage in multiple sclerosis and in its animal model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Here, we investigated whether glutamate receptor activation sensitizes oligodendrocytes to complement attack. We found that a brief incubation with glutamate followed by exposure to complement was lethal to oligodendrocytes in vitro and in freshly isolated optic nerves. Complement toxicity was induced by activation of kainate but not of AMPA receptors and was abolished by removing calcium from the medium during glutamate priming. Dose-response studies showed that sensitization to complement attack is induced by two distinct kainate receptor populations displaying high and low affinities for glutamate. Oligodendrocyte death by complement required the formation of the membrane attack complex, which in turn increased membrane conductance and induced calcium overload and mitochondrial depolarization as well as a rise in the level of reactive oxygen species. Treatment with the antioxidant Trolox and inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1, but not of caspases, protected oligodendrocytes against damage induced by complement. These findings indicate that glutamate sensitization of oligodendrocytes to complement attack may contribute to white matter damage in acute and chronic neurological disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Alberdi E, Sánchez-Gómez MV, Marino A, Matute C (2002). Ca2+ influx through AMPA or kainate receptors alone is sufficient to initiate excitotoxicity in cultured oligodendrocytes. Neurobiol Dis 9:234–243. - PubMed
-
- Barnett MH, Prineas JW (2004). Relapsing and remitting multiple sclerosis: pathology of the newly forming lesion. Ann Neurol 55:458–468. - PubMed
-
- Barnum SR (1995). Complement biosynthesis in the central nervous system. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 6:132–146. - PubMed
-
- Bohana-Kashtan O, Ziporen L, Donin N, Kraus S, Fishelson Z (2004). Cell signals transduced by complement. Mol Immunol 41:583–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
