Transgenic Hydra allow in vivo tracking of individual stem cells during morphogenesis
- PMID: 16556723
- PMCID: PMC1458856
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0510163103
Transgenic Hydra allow in vivo tracking of individual stem cells during morphogenesis
Abstract
Understanding the evolution of development in large part relies on the study of phylogenetically old organisms. Cnidarians, such as Hydra, have become attractive model organisms for these studies. However, despite long-term efforts, stably transgenic animals could not be generated, severely limiting the functional analysis of genes. Here we report the efficient generation of transgenic Hydra lines by embryo microinjection. One of these transgenic lines expressing EGFP revealed remarkably high motility of individual endodermal epithelial cells during morphogenesis. We expect that transgenic Hydra will become important tools to dissect the molecular mechanisms of development at the base of the Metazoan tree.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
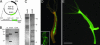
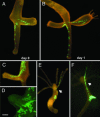

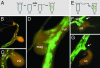
Comment in
-
Trembley's polyps go transgenic.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Apr 25;103(17):6415-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601983103. Epub 2006 Apr 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16618934 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Orr J. C., Fabry V. J., Aumont O., Bopp L., Doney S. C., Feely R. A., Gnanadesikan A., Gruber N., Ishida A., Joos F., et al. Nature. 2005;437:681–686. - PubMed
-
- Gierer A. Sci. Am. 1974;231:44–54. - PubMed
-
- Bosch T. C. G., Fujisawa T. BioEssays. 2001;23:420–427. - PubMed
-
- Galliot B., Schmid V. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2002;46:39–48. - PubMed
-
- Miller D. J., Ball E. E., Technau U. Trends Genet. 2005;21:536–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

