Simvastatin improves sepsis-induced mortality and acute kidney injury via renal vascular effects
- PMID: 16557230
- PMCID: PMC2377392
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000300
Simvastatin improves sepsis-induced mortality and acute kidney injury via renal vascular effects
Abstract
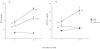
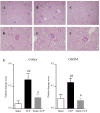
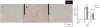
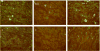
Acute kidney injury (AKI) occurs in about half of patients in septic shock and the mortality of AKI with sepsis is extremely high. An effective therapeutic intervention is urgently required. Statins are 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors that also have pleiotropic actions. They have been reported to increase the survival of septic or infectious patients. But the effect of simvastatin, a widely used statin, on sepsis-induced AKI is unknown. The effects of simvastatin and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha neutralizing antibody were studied in a clinically relevant model of sepsis-induced AKI using cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) in elderly mice. Simvastatin significantly improved CLP-induced mortality and AKI. Simvastatin attenuated CLP-induced tubular damage and reversed CLP-induced reduction of intrarenal microvascular perfusion and renal tubular hypoxia at 24 h. Simvastatin also restored towards normal CLP-induced renal vascular protein leak and serum TNF-alpha. Neither delayed simvastatin therapy nor TNF-alpha neutralizing antibody improved CLP-induced AKI. Simvastatin improved sepsis-induced AKI by direct effects on the renal vasculature, reversal of tubular hypoxia, and had a systemic anti-inflammatory effect.
Figures



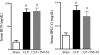
References
-
- Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R. Acute renal failure. Lancet. 2005;365:417–430. - PubMed
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. Jama. 2005;294:813–818. - PubMed
-
- Rangel-Frausto MS, Pittet D, Costigan M, et al. The natural history of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). A prospective study. Jama. 1995;273:117–123. - PubMed
-
- Neveu H, Kleinknecht D, Brivet F, et al. Prognostic factors in acute renal failure due to sepsis. Results of a prospective multicentre study. The French Study Group on Acute Renal Failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996;11:293–299. - PubMed
-
- Levy EM, Viscoli CM, Horwitz RI. The effect of acute renal failure on mortality. A cohort analysis. Jama. 1996;275:1489–1494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

