Essential role of TNF family molecule LIGHT as a cytokine in the pathogenesis of hepatitis
- PMID: 16557300
- PMCID: PMC1409742
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI27083
Essential role of TNF family molecule LIGHT as a cytokine in the pathogenesis of hepatitis
Abstract
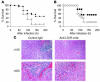
LIGHT is an important costimulatory molecule for T cell immunity. Recent studies have further implicated its role in innate immunity and inflammatory diseases, but its cellular and molecular mechanisms remain elusive. We report here that LIGHT is upregulated and functions as a proinflammatory cytokine in 2 independent experimental hepatitis models, induced by concanavalin A and Listeria monocytogenes. Molecular mutagenesis studies suggest that soluble LIGHT protein produced by cleavage from the cell membrane plays an important role in this effect through the interaction with the lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTbetaR) but not herpes virus entry mediator. NK1.1+ T cells contribute to the production, but not the cleavage or effector functions, of soluble LIGHT. Importantly, treatment with a mAb that specifically interferes with the LIGHT-LTbetaR interaction protects mice from lethal hepatitis. Our studies thus identify a what we believe to be a novel function of soluble LIGHT in vivo and offer a potential target for therapeutic interventions in hepatic inflammatory diseases.
Figures
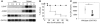



References
-
- Aggarwal B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:745–756. - PubMed
-
- Mauri D.N., et al. LIGHT, a new member of the TNF superfamily, and lymphotoxin alpha are ligands for herpesvirus entry mediator. Immunity. 1998;8:21–30. - PubMed
-
- Tamada K., et al. LIGHT, a TNF-like molecule, costimulates T cell proliferation and is required for dendritic cell-mediated allogeneic T cell response. J. Immunol. 2000;164:4105–4110. - PubMed
-
- Yu K.Y., et al. A newly identified member of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TR6) suppresses LIGHT-mediated apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:13733–13736. - PubMed
-
- Tamada K., et al. Modulation of T-cell-mediated immunity in tumor and graft-versus-host disease models through the LIGHT co-stimulatory pathway. Nat. Med. 2000;6:283–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

