The matrix-forming phenotype of cultured human meniscus cells is enhanced after culture with fibroblast growth factor 2 and is further stimulated by hypoxia
- PMID: 16563175
- PMCID: PMC1526627
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1929
The matrix-forming phenotype of cultured human meniscus cells is enhanced after culture with fibroblast growth factor 2 and is further stimulated by hypoxia
Abstract
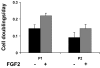
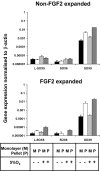
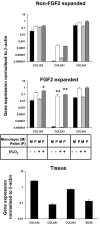
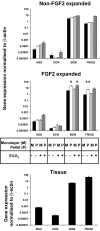
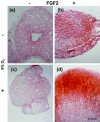
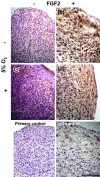
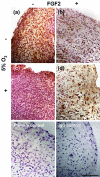
Human meniscus cells have a predominantly fibrogenic pattern of gene expression, but like chondrocytes they proliferate in monolayer culture and lose the expression of type II collagen. We have investigated the potential of human meniscus cells, which were expanded with or without fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), to produce matrix in three-dimensional cell aggregate cultures with a chondrogenic medium at low (5%) and normal (20%) oxygen tension. The presence of FGF2 during the expansion of meniscus cells enhanced the re-expression of type II collagen 200-fold in subsequent three-dimensional cell aggregate cultures. This was increased further (400-fold) by culture in 5% oxygen. Cell aggregates of FGF2-expanded meniscus cells accumulated more proteoglycan (total glycosaminoglycan) over 14 days and deposited a collagen II-rich matrix. The gene expression of matrix-associated proteoglycans (biglycan and fibromodulin) was also increased by FGF2 and hypoxia. Meniscus cells after expansion in monolayer can therefore respond to chondrogenic signals, and this is enhanced by FGF2 during expansion and low oxygen tension during aggregate cultures.
Figures
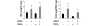
References
-
- Fithian DC, Kelly MA, Mow VC. Material properties and structure-function relationships in the menisci. Clin Orthop. 1990;252:19–31. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AM. The load-bearing role of the knee meniscus. In: Mow VC, Jackson DW, editor. Knee Meniscus: Basic and Clinical Foundations. New York: Raven Press; 1992. pp. 59–73.
-
- Levy IM, Torzilli PA, Fisch ID. The contribution of the menisci to the stability of the knee. In: Mow VC, Jackson DW, editor. Knee Meniscus: Basic and Clinical Foundations. New York: Raven Press; 1992. pp. 107–115.
-
- Fairbank T. Knee joint changes after menisectomy. J Bone Joint Surg. 1948;30B:664–670. - PubMed
-
- Cox JS, Nye CE, Schaefer WW, Woodstein IJ. The degenerative effects of partial and total resection of the medial meniscus in dogs' knees. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975;109:178–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

