Health risks at the Hajj
- PMID: 16564364
- PMCID: PMC7137144
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68429-8
Health risks at the Hajj
Abstract
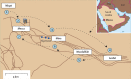
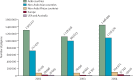
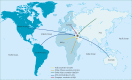
Annually, millions of Muslims embark on a religious pilgrimage called the "Hajj" to Mecca in Saudi Arabia. The mass migration during the Hajj is unparalleled in scale, and pilgrims face numerous health hazards. The extreme congestion of people and vehicles during this time amplifies health risks, such as those from infectious diseases, that vary each year. Since the Hajj is dictated by the lunar calendar, which is shorter than the Gregorian calendar, it presents public-health policy planners with a moving target, demanding constant preparedness. We review the communicable and non-communicable hazards that pilgrims face. With the rise in global travel, preventing disease transmission has become paramount to avoid the spread of infectious diseases, including SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome), avian influenza, and haemorrhagic fever. We examine the response of clinicians, the Saudi Ministry of Health, and Hajj authorities to these unique problems, and list health recommendations for prospective pilgrims.
Figures
Comment in
-
Meningococcal vaccine coverage in Hajj pilgrims.Lancet. 2007 Apr 21;369(9570):1343. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60625-4. Lancet. 2007. PMID: 17448813 No abstract available.
References
-
- Memish ZA. Infection control in Saudi Arabia: meeting the challenge. Am J Infect Control. 2002;30:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Memish ZA, Venkatesh S, Ahmed QA. Travel epidemiology: the Saudi perspective. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2003;21:96–101. - PubMed
-
- Health conditions for travellers to Saudi Arabia pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2005;80:431–432. - PubMed
-
- Risk for meningococcal disease associated with the Hajj 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50:97–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous