Potential prognostic value of leptin receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 16565226
- PMCID: PMC1860536
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2005.033464
Potential prognostic value of leptin receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Obesity is associated with several human malignancies, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This association may result from the deregulated expression of adipokines.
Aims: To explore the potential role and the prognostic value of leptin receptor (Ob-R) in HCC.
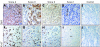
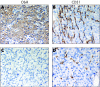
Methods: 66 patients with pathologically confirmed HCC were included in this study. Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the expression of Ob-R, microvessel density (MVD) and Ki-67 index in these patients. Eventually, the profiles of Ob-R expression, obtained by a semiquantitative scoring system, were further correlated with Ki-67 expression, intratumour MVD, clinicopathological characteristics and overall survival.
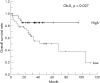
Results: High Ob-R expression was seen in 53% of patients with HCC and was significantly correlated with intratumour MVD (high v low; 59.4 (3.2) v 44.7 (3.7); p = 0.004), but not with Ki-67 expression. In addition, Ob-R expression was inversely correlated with vascular invasion (p = 0.037), but not with other known clinicopathological characteristics. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve showed that high Ob-R expression was associated with a better overall survival (p = 0.027). Meanwhile, multivariate analysis showed that Ob-R expression was a significant determinant for HCC (odds ratio 0.02, 95% confidence interval 0.01 to 0.85; p = 0.041).
Conclusion: Ob-R expression may have a potential role in the carcinogenesis of HCC. The positive association of Ob-R expression in the cancerous lesions of HCC with the survival outcome can be explained by its inverse correlation with vascular invasion, and may have prognostic value in HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Peto J. Cancer epidemiology in the last century and the next decade. Nature 2001411390–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous