Lipoxin A(4) regulates bronchial epithelial cell responses to acid injury
- PMID: 16565483
- PMCID: PMC1606555
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051056
Lipoxin A(4) regulates bronchial epithelial cell responses to acid injury
Abstract
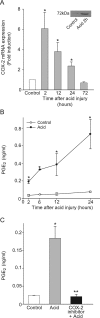
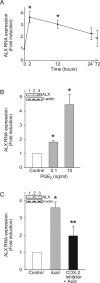
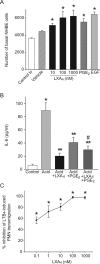
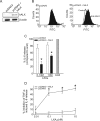
Aspiration of gastric acid commonly injures airway epithelium and, if severe, can lead to respiratory failure from acute respiratory distress syndrome. Recently, we identified cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-derived prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and lipoxin A(4) (LXA(4)) as pivotal mediators in vivo for resolution of acid-initiated acute lung injury. To examine protective mechanisms for these mediators in the airway, we developed an in vitro model of acid injury by transiently exposing well-differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial cells to hydrochloric acid. Transmission electron microscopy revealed selective injury to superficial epithelial cells with disruption of cell attachments and cell shedding. The morphological features of injury were substantially resolved within 6 hours. Acid triggered and early marked increases in COX-2 expression and PGE(2) production, and acid-induced PGE(2) significantly increased epithelial LXA(4) receptor (ALX) expression. LXA(4) is generated in vivo during acute lung injury, and we observed that nanomolar quantities increased basal epithelial cell proliferation and potently blocked acid-triggered interleukin-6 release and neutrophil transmigration across well-differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Expression of recombinant human ALX in A549 airway epithelial cells uncovered ALX-dependent inhibition of cytokine release by LXA(4). Together, these findings indicate that injured bronchial epithelial cells up-regulate ALX in a COX-2-dependent manner to promote LXA(4)-mediated resolution of airway inflammation.
Figures

Comment in
-
Commonality of defensive roles of COX-2 in the lung and gut.Am J Pathol. 2006 Apr;168(4):1060-3. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060023. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16565482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Commonality of defensive roles of COX-2 in the lung and gut.Am J Pathol. 2006 Apr;168(4):1060-3. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060023. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16565482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Synthesis and anti-inflammatory effect of lipoxins in human airway epithelial cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2007 Jun;61(5):261-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2007.02.016. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17418999
-
Lipoxin A₄-mediated KATP potassium channel activation results in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial repair.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 Jul 15;305(2):L193-201. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00058.2013. Epub 2013 May 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23686859
-
Lipoxins in asthma: potential therapeutic mediators on bronchial inflammation?Allergy. 2004 Oct;59(10):1027-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2004.00617.x. Allergy. 2004. PMID: 15355460 Review.
-
The lipoxin receptor ALX: potent ligand-specific and stereoselective actions in vivo.Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):463-87. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.4. Pharmacol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16968948 Review.
Cited by
-
Commonality of defensive roles of COX-2 in the lung and gut.Am J Pathol. 2006 Apr;168(4):1060-3. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060023. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16565482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Aspirin-triggered lipoxin and resolvin E1 modulate vascular smooth muscle phenotype and correlate with peripheral atherosclerosis.Am J Pathol. 2010 Oct;177(4):2116-23. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.091082. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20709806 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxin A4 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury through stimulating epithelial proliferation, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Respir Res. 2019 Aug 22;20(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1158-z. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31438948 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels in articular chondrocytes by amiloride attenuates articular cartilage destruction in rats with adjuvant arthritis.Inflamm Res. 2010 Nov;59(11):939-47. doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0206-4. Epub 2010 May 8. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 20454829
-
Novel biphasic role of LipoxinA(4) on expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated lung fibroblasts.Mediators Inflamm. 2011;2011:745340. doi: 10.1155/2011/745340. Epub 2011 Jul 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2011. PMID: 21765620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nathan C. Points of control in inflammation. Nature. 2002;420:846–852. - PubMed
-
- Wynne JW, Ramphal R, Hood CI. Tracheal mucosal damage after aspiration. A scanning electron microscope study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981;124:728–732. - PubMed
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1334–1349. - PubMed
-
- Samuelsson B, Dahlen SE, Lindgren JA, Rouzer CA, Serhan CN. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 1987;237:1171–1176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

