Activation of the canonical wingless/T-cell factor signaling pathway promotes invasive differentiation of human trophoblast
- PMID: 16565489
- PMCID: PMC1606554
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050686
Activation of the canonical wingless/T-cell factor signaling pathway promotes invasive differentiation of human trophoblast
Abstract
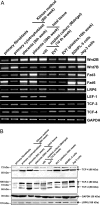
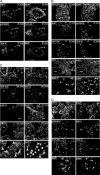
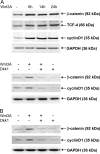
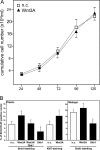
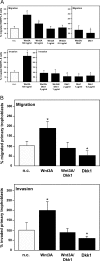
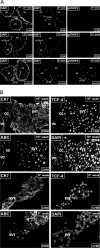
The molecular mechanisms governing invasive differentiation of human trophoblasts remain largely elusive. Here, we investigated the role of Wnt-beta-catenin-T-cell factor (TCF) signaling in this process. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analyses demonstrated expression of Wnt ligands, frizzled receptors, LRP-6, and TCF-3/4 transcription factors in total placenta and different trophoblast cell models. Immunohistochemistry of placental tissues and differentiating villous explant cultures showed that expression of TCF-3/4 strongly increased in invading trophoblasts. Some of these cells also accumulated dephosphorylated beta-catenin in the nucleus. Wnt3A treatment of primary cytotrophoblasts and SGHPL-5 cells induced activity of TCF-luciferase reporters. Accordingly, the ligand provoked interaction of TCF-3/4 with beta-catenin as assessed in electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) and up-regulation of Wnt/TCF target genes as observed by Western blot analyses. Wnt3A stimulated trophoblast migration and invasion through Matrigel, which could be blocked by addition of Dickkopf-1, mediating in-hibition of canonical Wnt signaling. Dickkopf-1 also reduced basal migration, invasion, and proliferation of cytotrophoblasts, suggesting expression of endogenous Wnt ligand(s). Immunohistochemistry revealed that the percentage of extravillous trophoblasts containing nuclear beta-catenin was significantly higher in placentas of complete hydatidiform mole pregnancies as compared to normal placentas. Thus, canonical Wnt signaling may promote invasive trophoblast differentiation, and exaggerated activation of the path-way could contribute to trophoblastic hyperplasia and local invasion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Wingless (Wnt)-3A induces trophoblast migration and matrix metalloproteinase-2 secretion through canonical Wnt signaling and protein kinase B/AKT activation.Endocrinology. 2010 Jan;151(1):211-20. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0557. Epub 2009 Nov 3. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 19887570 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt-dependent T-cell factor-4 controls human etravillous trophoblast motility.Endocrinology. 2014 May;155(5):1908-20. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-2042. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24605829
-
Wnt antagonism inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008 Jan;294(1):G39-49. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00263.2007. Epub 2007 Nov 15. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18006602
-
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases.Dev Cell. 2009 Jul;17(1):9-26. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.016. Dev Cell. 2009. PMID: 19619488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in trophoblasts and abnormal activation in preeclampsia (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2017 Aug;16(2):1007-1013. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6718. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 29067442 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression pattern and function of Notch2 in different subtypes of first trimester cytotrophoblast.Placenta. 2015 Apr;36(4):365-71. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Placenta. 2015. PMID: 25659500 Free PMC article.
-
Folate protection from congenital heart defects linked with canonical Wnt signaling and epigenetics.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010 Oct;22(5):561-6. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e32833e2723. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010. PMID: 20844350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFPA Award in Placentology lecture: molecular regulation of human trophoblast invasion.Placenta. 2012 Feb;33 Suppl(2):S55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.09.019. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Placenta. 2012. PMID: 22019198 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperactivated Wnt-β-catenin signaling in the absence of sFRP1 and sFRP5 disrupts trophoblast differentiation through repression of Ascl2.BMC Biol. 2020 Oct 27;18(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00883-4. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 33109217 Free PMC article.
-
YAP-mediated trophoblast dysfunction: the common pathway underlying pregnancy complications.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Dec 14;21(1):353. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01371-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38098027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pijnenborg R, Bland JM, Robertson WB, Brosens I. Uteroplacental arterial changes related to interstitial trophoblast migration in early human pregnancy. Placenta. 1983;4:397–413. - PubMed
-
- Vicovac L, Jones CJ, Aplin JD. Trophoblast differentiation during formation of anchoring villi in a model of the early human placenta in vitro. Placenta. 1995;16:41–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

