Therapeutic effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: down-regulation of inflammatory and autoimmune responses
- PMID: 16565493
- PMCID: PMC1606545
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051081
Therapeutic effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: down-regulation of inflammatory and autoimmune responses
Abstract
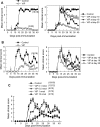
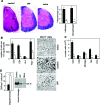
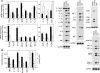
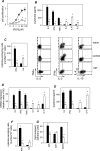
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disabling inflammatory, autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. Despite intensive investigation, the mechanisms of disease pathogenesis remain unclear, and curative therapies are unavailable for MS. The current study describes a possible new strategy for the treatment of MS, based on the administration of the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), a well-known immunosuppressive neuropeptide. Treatment with VIP significantly reduced incidence and severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), in a MS-related rodent model system. VIP suppressed EAE neuropathology by reducing central nervous system inflammation, including the regulation of a wide spectrum of inflammatory mediators, and by selectively blocking encephalitogenic T-cell reactivity. Importantly, VIP treatment was therapeutically effective in established EAE and prevented the recurrence of the disease. Consequently, VIP represents a novel multistep therapeutic approach for the future treatment of human MS.
Figures
References
-
- Steinman L. Assessment of animal models for MS and demyelinating disease in the design of rational therapy. Neuron. 1999;24:511–514. - PubMed
-
- Bauer J, Rauschka H, Lassmann H. Inflammation in the nervous system: the human perspective. Glia. 2001;36:235–243. - PubMed
-
- Owens T. The enigma of multiple sclerosis: inflammation and neurodegeneration cause heterogeneous dysfunction and damage. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003;16:259–265. - PubMed
-
- Pozo D, Delgado M. The many faces of vasoactive intestinal peptide in neuroimmunology: a cytokine rather a neuropeptide? FASEB J. 2004;18:1325–1334. - PubMed
-
- Delgado M, Pozo D, Ganea D. The significance of the vasoactive intestinal peptide in immunomodulation. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:249–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

