Chemical modulation of receptor signaling inhibits regenerative angiogenesis in adult zebrafish
- PMID: 16565716
- PMCID: PMC1534118
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio778
Chemical modulation of receptor signaling inhibits regenerative angiogenesis in adult zebrafish
Abstract
We examined the role of angiogenesis and the need for receptor signaling using chemical inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor in the adult zebrafish tail fin. Using a small-molecule inhibitor, we were able to exert precise control over blood vessel regeneration. An angiogenic limit to tissue regeneration was determined, as avascular tissue containing skin, pigment, neuronal axons and bone precursors could regenerate up to about 1 mm. This indicates that tissues can regenerate without direct interaction with endothelial cells and at a distance from blood supply. We also investigated whether the effects of chemical inhibition could be enhanced in zebrafish vascular mutants. We found that adult zebrafish, heterozygous for a mutation in the critical receptor effector phospholipase Cgamma1, show a greater sensitivity to chemical inhibition. This study illustrates the utility of the adult zebrafish as a new model system for receptor signaling and chemical biology.
Figures

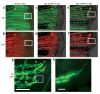

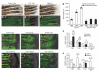
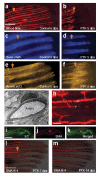
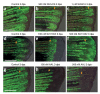
Comment in
-
Fishing and frogging for anti-angiogenic drugs.Nat Chem Biol. 2006 May;2(5):228-9. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0506-228. Nat Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 16619017 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chanda SK. Fulfilling the promise: drug discovery in the post-genomic era. Drug Discov. Today. 2003;8:168–174. - PubMed
-
- Drews J. Drug discovery: a historical perspective. Science. 2000;287:1960–1964. - PubMed
-
- Lenz GR. Chemical ligands, genomics, and drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today. 2000;5:145–156. - PubMed
-
- Zon LI, Peterson RT. In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4:35–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases

