Neutrophil-derived leukotriene B4 is required for inflammatory arthritis
- PMID: 16567388
- PMCID: PMC2118292
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20052371
Neutrophil-derived leukotriene B4 is required for inflammatory arthritis
Abstract
Neutrophils serve as a vanguard of the acute innate immune response to invading pathogens. Neutrophils are also abundant at sites of autoimmune inflammation, such as the rheumatoid joint, although their pathophysiologic role is incompletely defined and relevant effector functions remain obscure. Using genetic and pharmacologic approaches in the K/BxN serum transfer model of arthritis, we find that autoantibody-driven erosive synovitis is critically reliant on the generation of leukotrienes, and more specifically on leukotriene B4 (LTB4), for disease induction as well as perpetuation. Pursuing the cellular source for this mediator, we find via reconstitution experiments that mast cells are a dispensable source of leukotrienes, whereas arthritis susceptibility can be restored to leukotriene-deficient mice by intravenous administration of wild-type neutrophils. These experiments demonstrate a nonredundant role for LTB4 in inflammatory arthritis and define a neutrophil mediator involved in orchestrating the synovial eruption.
Figures
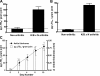

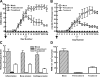

References
-
- Edwards, S.W., and M.B. Hallett. 1997. Seeing the wood for the trees: the forgotten role of neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Today. 18:320–324. - PubMed
-
- Koshihara, Y., T. Isono, H. Oda, S. Karube, and Y. Hayashi. 1988. Measurement of sulfidopeptide leukotrienes and their metabolism in human synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 32:113–119. - PubMed
-
- Korganow, A.S., H. Ji, S. Mangialaio, V. Duchatelle, R. Pelanda, T. Martin, C. Degott, H. Kikutani, K. Rajewsky, J.L. Pasquali, et al. 1999. From systemic T cell self-reactivity to organ-specific autoimmune disease via immunoglobulins. Immunity. 10:451–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

