A protein interaction surface in nonribosomal peptide synthesis mapped by combinatorial mutagenesis and selection
- PMID: 16567620
- PMCID: PMC1459352
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0601038103
A protein interaction surface in nonribosomal peptide synthesis mapped by combinatorial mutagenesis and selection
Abstract
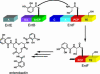
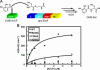
Nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) and polyketide synthases are large, multidomain enzymes that biosynthesize a number of pharmaceutically important natural products. The recognition of biosynthetic intermediates, displayed via covalent attachment to carrier proteins, by catalytic domains is critical for NRPS and polyketide synthase function. We report the use of combinatorial mutagenesis coupled with in vivo selection for the production of the Escherichia coli NRPS product enterobactin to map the surface of the aryl carrier protein (ArCP) domain of EntB that interacts with the downstream elongation module EntF. Two libraries spanning the predicted helix 2 and loop 2/helix 3 of EntB-ArCP were generated by shotgun alanine scanning and selected for their ability to support enterobactin production. From the surviving pools, we identified several hydrophobic residues (M249, F264, and A268) that were highly conserved. These residues cluster near the phosphopantetheinylated serine in a structural model, and two of these positions are in the predicted helix 3 region. Subsequent in vitro studies are consistent with the hypothesis that these residues form a surface on EntB required for interaction with EntF. These results suggest that helix 3 is a major recognition element in EntB-ArCP and demonstrate the utility of selection-based approaches for studying NRPS biosynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

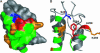
Similar articles
-
Localized protein interaction surfaces on the EntB carrier protein revealed by combinatorial mutagenesis and selection.J Am Chem Soc. 2006 Aug 30;128(34):11002-3. doi: 10.1021/ja063238h. J Am Chem Soc. 2006. PMID: 16925399
-
Assembly line enzymology by multimodular nonribosomal peptide synthetases: the thioesterase domain of E. coli EntF catalyzes both elongation and cyclolactonization.Chem Biol. 1999 Jun;6(6):385-400. doi: 10.1016/S1074-5521(99)80050-7. Chem Biol. 1999. PMID: 10375542
-
Dissection of the EntF condensation domain boundary and active site residues in nonribosomal peptide synthesis.Biochemistry. 2003 Feb 11;42(5):1334-44. doi: 10.1021/bi026867m. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12564937
-
Ways of assembling complex natural products on modular nonribosomal peptide synthetases.Chembiochem. 2002 Jun 3;3(6):490-504. doi: 10.1002/1439-7633(20020603)3:6<490::AID-CBIC490>3.0.CO;2-N. Chembiochem. 2002. PMID: 12325005 Review.
-
Nonribosomal peptide synthetases: structures and dynamics.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010 Apr;20(2):234-40. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010. PMID: 20153164 Review.
Cited by
-
FRET Monitoring of a Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Elongation Module Reveals Carrier Protein Shuttling between Catalytic Domains.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Nov 25;61(48):e202212994. doi: 10.1002/anie.202212994. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 36169151 Free PMC article.
-
Explorations of catalytic domains in non-ribosomal peptide synthetase enzymology.Nat Prod Rep. 2012 Oct;29(10):1074-98. doi: 10.1039/c2np20025b. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Nat Prod Rep. 2012. PMID: 22802156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathogen-associated iroA gene cluster mediates bacterial evasion of lipocalin 2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Oct 31;103(44):16502-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604636103. Epub 2006 Oct 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17060628 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Biology of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1401:3-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3375-4_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26831698 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and biochemical analyses of chromosome and plasmid gene homologues encoding ICL and ArCP domains in Vibrio anguillarum strain 775.Biometals. 2011 Aug;24(4):629-43. doi: 10.1007/s10534-011-9416-7. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Biometals. 2011. PMID: 21286786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cane D. E., Walsh C. T., Khosla C. Science. 1998;282:63–68. - PubMed
-
- Pieper R., Luo G., Cane D. E., Khosla C. Nature. 1995;378:263–266. - PubMed
-
- Hubbard B. K., Walsh C. T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2003;42:730–765. - PubMed
-
- Tang L., Shah S., Chung L., Carney J., Katz L., Khosla C., Julien B. Science. 2000;287:640–642. - PubMed
-
- Shen B., Du L., Sanchez C., Edwards D. J., Chen M., Murrell J. M. J. Nat. Prod. 2002;65:422–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

