Relations between neighborhood factors, parenting behaviors, peer deviance, and delinquency among serious juvenile offenders
- PMID: 16569170
- PMCID: PMC2791995
- DOI: 10.1037/0012-1649.42.2.319
Relations between neighborhood factors, parenting behaviors, peer deviance, and delinquency among serious juvenile offenders
Abstract
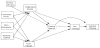
The present study examined relations among neighborhood structural and social characteristics, parenting practices, peer group affiliations, and delinquency among a group of serious adolescent offenders. The sample of 14-18-year-old boys (N=488) was composed primarily of economically disadvantaged, ethnic-minority youth living in urban communities. The results indicate that weak neighborhood social organization is indirectly related to delinquency through its associations with parenting behavior and peer deviance and that a focus on just 1 of these microsystems can lead to oversimplified models of risk for juvenile offending. The authors also find that community social ties may confer both pro- and antisocial influences to youth, and they advocate for a broad conceptualization of neighborhood social processes as these relate to developmental risk for youth living in disadvantaged communities.
Copyright (c) 2006 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson E. Code of the streets: Decency, violence, and the moral life of the inner city. New York: Norton; 1999.
-
- Arbuckle JL. AMOS for Windows: Analysis of moment structures (Version 5) [Computer software and manual] Chicago: Smallwaters; 1999.
-
- Barcikowski RS. Statistical power with a group mean as a unit of analysis. Journal of Educational Statistics. 1981;6:267–285.
-
- Baron RM, Kenny D. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Bellair P. Social interaction and community crime: Examining the importance of neighborhood networks. Criminology. 1997;35:677–703.

